The Milky Way is less massive than astronomers previously thought, according to new research. For the first time, scientists have been able to precisely measure the mass of the galaxy that contains our Solar system.
Jul 30th, 2014
Read more
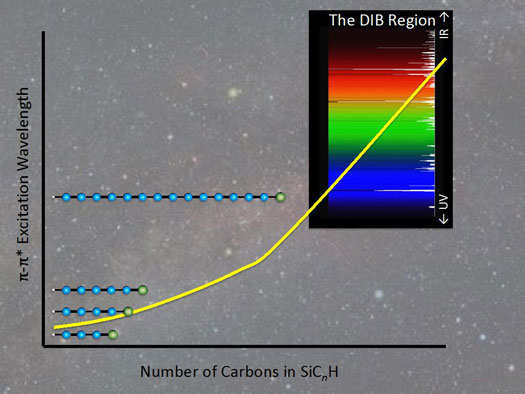 A group of scientists has offered a tantalizing new possibility: these mysterious molecules may be silicon-capped hydrocarbons like SiC3H, SiC4H and SiC5H, and they present data and theoretical arguments to back that hypothesis.
A group of scientists has offered a tantalizing new possibility: these mysterious molecules may be silicon-capped hydrocarbons like SiC3H, SiC4H and SiC5H, and they present data and theoretical arguments to back that hypothesis.
Jul 29th, 2014
Read more
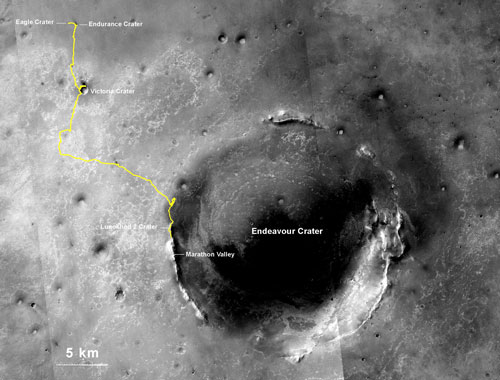 NASA's Opportunity Mars rover, which landed on the Red Planet in 2004, now holds the off-Earth roving distance record after accruing 25 miles (40 kilometers) of driving. The previous record was held by the Soviet Union's Lunokhod 2 rover.
NASA's Opportunity Mars rover, which landed on the Red Planet in 2004, now holds the off-Earth roving distance record after accruing 25 miles (40 kilometers) of driving. The previous record was held by the Soviet Union's Lunokhod 2 rover.
Jul 28th, 2014
Read more
 A team of international researchers has discovered a new type of cool burning flames that could lead to cleaner, more efficient engines for cars. The discovery was made during a series of experiments on the International Space Station.
A team of international researchers has discovered a new type of cool burning flames that could lead to cleaner, more efficient engines for cars. The discovery was made during a series of experiments on the International Space Station.
Jul 28th, 2014
Read more
 Following the approval of a sublease on July 25 by the Hawaii Board of Land and Natural Resources, the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) announces the beginning of the construction phase on Hawaii Island.
Following the approval of a sublease on July 25 by the Hawaii Board of Land and Natural Resources, the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) announces the beginning of the construction phase on Hawaii Island.
Jul 28th, 2014
Read more
 A recent study shows that the emission is dominated by the local hot bubble of gas - 1 million degrees - with, at most, 40 percent of emission originating within the solar system. The findings should put to rest the disagreement about the origin of the X-ray emission and confirm the existence of the local hot bubble.
A recent study shows that the emission is dominated by the local hot bubble of gas - 1 million degrees - with, at most, 40 percent of emission originating within the solar system. The findings should put to rest the disagreement about the origin of the X-ray emission and confirm the existence of the local hot bubble.
Jul 28th, 2014
Read more
 OSIRIS images of Rosetta's comet resolve structures at 100 metres pixel scale.
OSIRIS images of Rosetta's comet resolve structures at 100 metres pixel scale.
Jul 24th, 2014
Read more
 Astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope have mapped the mass within a galaxy cluster more precisely than ever before. Created using observations from Hubble's Frontier Fields observing programme, the map shows the amount and distribution of mass within MCS J0416.1-2403, a massive galaxy cluster found to be 160 trillion times the mass of the Sun.
Astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope have mapped the mass within a galaxy cluster more precisely than ever before. Created using observations from Hubble's Frontier Fields observing programme, the map shows the amount and distribution of mass within MCS J0416.1-2403, a massive galaxy cluster found to be 160 trillion times the mass of the Sun.
Jul 24th, 2014
Read more
 Astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have gone looking for water vapor in the atmospheres of three planets orbiting stars similar to the sun - and have come up nearly dry.
Astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have gone looking for water vapor in the atmospheres of three planets orbiting stars similar to the sun - and have come up nearly dry.
Jul 24th, 2014
Read more
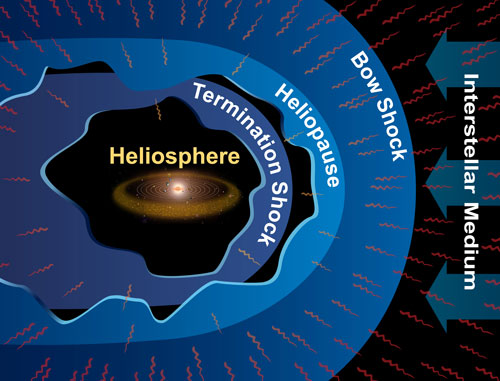 In 2012, the Voyager mission team announced that the Voyager 1 spacecraft had passed into interstellar space, traveling further from Earth than any other manmade object. But, in the nearly two years since that historic announcement, and despite subsequent observations backing it up, uncertainty about whether Voyager 1 really crossed the threshold continues.
In 2012, the Voyager mission team announced that the Voyager 1 spacecraft had passed into interstellar space, traveling further from Earth than any other manmade object. But, in the nearly two years since that historic announcement, and despite subsequent observations backing it up, uncertainty about whether Voyager 1 really crossed the threshold continues.
Jul 23rd, 2014
Read more
 An international team of researchers has studied 380 galaxies and shown that their small satellite galaxies almost always move in rotating discs. However, such satellite galaxy discs are not predicted by current models of the formation of structures in the Universe. This discovery could cause modelers serious headaches in the years ahead.
An international team of researchers has studied 380 galaxies and shown that their small satellite galaxies almost always move in rotating discs. However, such satellite galaxy discs are not predicted by current models of the formation of structures in the Universe. This discovery could cause modelers serious headaches in the years ahead.
Jul 23rd, 2014
Read more
 Humanity is on the threshold of being able to detect signs of alien life on other worlds. By studying exoplanet atmospheres, we can look for gases like oxygen and methane that only coexist if replenished by life. But those gases come from simple life forms like microbes. What about advanced civilizations? Would they leave any detectable signs? They might, if they spew industrial pollution into the atmosphere.
Humanity is on the threshold of being able to detect signs of alien life on other worlds. By studying exoplanet atmospheres, we can look for gases like oxygen and methane that only coexist if replenished by life. But those gases come from simple life forms like microbes. What about advanced civilizations? Would they leave any detectable signs? They might, if they spew industrial pollution into the atmosphere.
Jul 23rd, 2014
Read more
 New work compares the chemical composition of Titan's atmosphere with parameters predicted by a mathematical model.
New work compares the chemical composition of Titan's atmosphere with parameters predicted by a mathematical model.
Jul 23rd, 2014
Read more
A new home-grown instrument based on bundles of optical fibres is giving Australian astronomers the first 'Google street view' of the cosmos - incredibly detailed views of huge numbers of galaxies.
Jul 23rd, 2014
Read more
 In this new image from La Silla Observatory in Chile young stars huddle together against clouds of glowing gas and lanes of dust. The star cluster, NGC 3293, would have been just a cloud of gas and dust itself about ten million years ago, but as stars began to form it became the bright group of stars we see here. Clusters like this are laboratories that allow astronomers to learn about how stars evolve.
In this new image from La Silla Observatory in Chile young stars huddle together against clouds of glowing gas and lanes of dust. The star cluster, NGC 3293, would have been just a cloud of gas and dust itself about ten million years ago, but as stars began to form it became the bright group of stars we see here. Clusters like this are laboratories that allow astronomers to learn about how stars evolve.
Jul 23rd, 2014
Read more
 In late June 2013, an exceptional binary containing a rapidly spinning neutron star underwent a dramatic change in behavior never before observed. The pulsar's radio beacon vanished, while at the same time the system brightened fivefold in gamma rays, the most powerful form of light, according to measurements by the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope.
In late June 2013, an exceptional binary containing a rapidly spinning neutron star underwent a dramatic change in behavior never before observed. The pulsar's radio beacon vanished, while at the same time the system brightened fivefold in gamma rays, the most powerful form of light, according to measurements by the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope.
Jul 23rd, 2014
Read more
 Astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope have probed the extreme outskirts of the stunning elliptical galaxy Centaurus A. The galaxy's halo of stars has been found to extend much further from the galaxy's centre than expected and the stars within this halo seem to be surprisingly rich in heavy elements. This is the most remote portion of an elliptical galaxy ever to have been explored.
Astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope have probed the extreme outskirts of the stunning elliptical galaxy Centaurus A. The galaxy's halo of stars has been found to extend much further from the galaxy's centre than expected and the stars within this halo seem to be surprisingly rich in heavy elements. This is the most remote portion of an elliptical galaxy ever to have been explored.
Jul 22nd, 2014
Read more
Astronomers have discovered a transiting exoplanet with the longest known year. Kepler-421b circles its star once every 704 days. In comparison, Mars orbits our Sun once every 780 days. Most of the 1,800-plus exoplanets discovered to date are much closer to their stars and have much shorter orbital periods.
Jul 21st, 2014
Read more

 Subscribe to our Space Exploration News feed
Subscribe to our Space Exploration News feed













