Microelectronics: Automating cancer detection
A sensor developed at A*STAR can detect bladder cancer cells and track tumor progression.
Aug 14th, 2013
Read more
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
A sensor developed at A*STAR can detect bladder cancer cells and track tumor progression.
Aug 14th, 2013
Read moreA microchip that can identify human pathogens in a single test could revolutionize the diagnosis of infections.
Aug 14th, 2013
Read moreResearchers have now created the first simplified computer model of the process that forms the Fahraeus-Lindqvist layer in our blood -- a model that could help to improve the design of artificial platelets and medical treatments for trauma injuries and for blood disorders such as sickle cell anemia and malaria.
Aug 13th, 2013
Read moreUsing human pluripotent stem cells and DNA-cutting protein from meningitis bacteria, researchers from the Morgridge Institute for Research and Northwestern University have created an efficient way to target and repair defective genes.
Aug 13th, 2013
Read more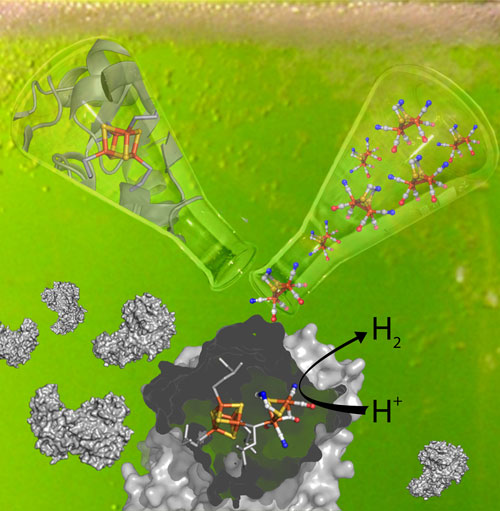 Scientists have discovered an efficient process for hydrogen biocatalysis. They developed semi-synthetic hydrogenases, hydrogen-generating enzymes, by adding the protein's biological precursor to a chemically synthesized inactive iron complex. From these two components, the biological catalyst formed spontaneously in a test tube.
Scientists have discovered an efficient process for hydrogen biocatalysis. They developed semi-synthetic hydrogenases, hydrogen-generating enzymes, by adding the protein's biological precursor to a chemically synthesized inactive iron complex. From these two components, the biological catalyst formed spontaneously in a test tube.
Aug 12th, 2013
Read more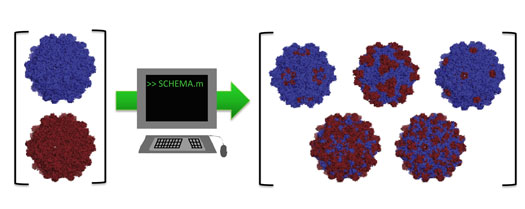 Researchers are making strides toward a set of rules to custom-design Lego-like viral capsid proteins for gene therapy.
Researchers are making strides toward a set of rules to custom-design Lego-like viral capsid proteins for gene therapy.
Aug 12th, 2013
Read more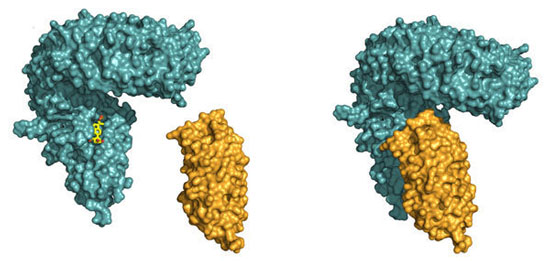 Researchers resolve how a plant steroid hormone makes plants grow.
Researchers resolve how a plant steroid hormone makes plants grow.
Aug 8th, 2013
Read moreA scientific breakthrough by researchers at the University of Kent has revealed how vitamin B12/antipernicious anaemia factor is made - a challenge often referred to as 'the Mount Everest of biosynthetic problems'.
Aug 8th, 2013
Read more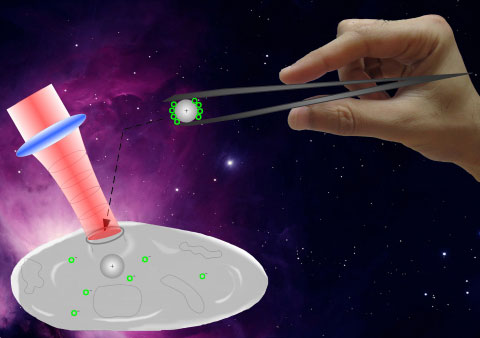 The method combines two high-tech laboratory techniques and allows the researchers to precisely poke holes on the surface of a single cell with a high-powered femtosecond laser and then gently tug a piece of DNA through it using optical tweezers, which draw on the electromagnetic field of another laser.
The method combines two high-tech laboratory techniques and allows the researchers to precisely poke holes on the surface of a single cell with a high-powered femtosecond laser and then gently tug a piece of DNA through it using optical tweezers, which draw on the electromagnetic field of another laser.
Aug 8th, 2013
Read more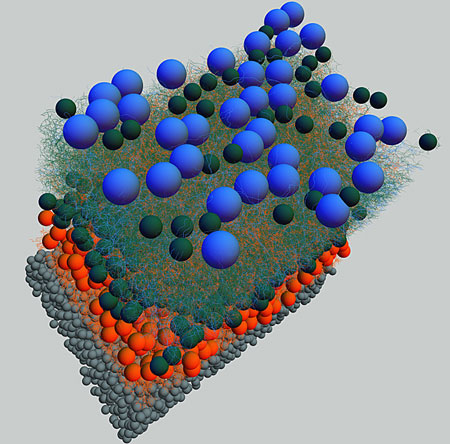 Wiring diagram of retinal neurons is first step toward mapping the human brain.
Wiring diagram of retinal neurons is first step toward mapping the human brain.
Aug 7th, 2013
Read more A microorganism living in Trondheim Fjord will provide you with better protection against skin cancer and malignant melanomas.
A microorganism living in Trondheim Fjord will provide you with better protection against skin cancer and malignant melanomas.
Aug 6th, 2013
Read more By adding covalent bonds to proteins, researchers can design new drugs, imaging agents, or molecules that aid basic research.
By adding covalent bonds to proteins, researchers can design new drugs, imaging agents, or molecules that aid basic research.
Aug 5th, 2013
Read more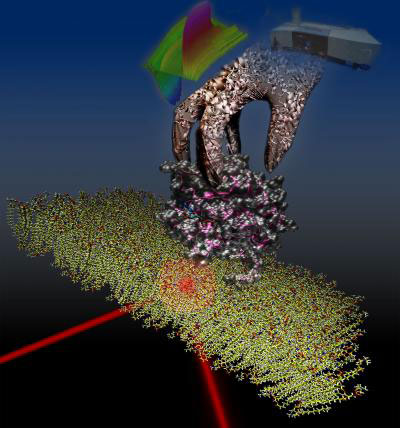 Researchers have for the first time successfully reproduced the recycling process of proteins regulating cellular transport in a biophysical experiment.
Researchers have for the first time successfully reproduced the recycling process of proteins regulating cellular transport in a biophysical experiment.
Aug 5th, 2013
Read moreScientists on Monday unveiled the world's first lab-grown beef burger, serving it up to volunteers in London in what they hope is the start of a food revolution.
Aug 5th, 2013
Read more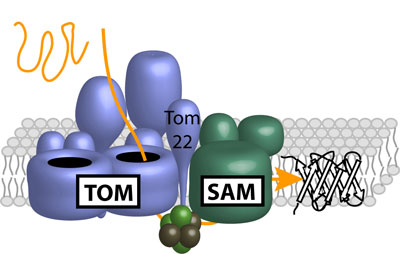 Researchers show that two protein machineries collaborate on the development of barrel structures in the mitochondria.
Researchers show that two protein machineries collaborate on the development of barrel structures in the mitochondria.
Aug 5th, 2013
Read moreBy borrowing a tool from bacteria that infect plants, scientists have developed a new approach to eliminate mutated DNA inside mitochondria - the energy factories within cells. Doctors might someday use the approach to treat a variety of mitochondrial diseases, including the degenerative eye disease Leber hereditary optic neuropathy.
Aug 4th, 2013
Read more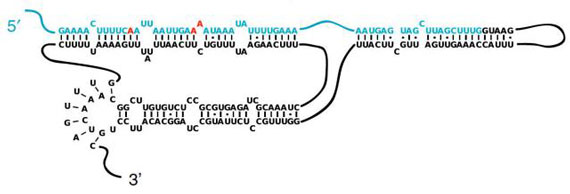 A new study finds that RNA editing is not only regulated by sequences and structures near the editing sites but also by ones found much farther away. One newly discovered structure gives an editing enzyme an alternate docking site. The other appears to throttle competing splicing activity.
A new study finds that RNA editing is not only regulated by sequences and structures near the editing sites but also by ones found much farther away. One newly discovered structure gives an editing enzyme an alternate docking site. The other appears to throttle competing splicing activity.
Aug 1st, 2013
Read moreScientists have developed a model that makes predictions from which differentiated cells - for instance skin cells - can be very efficiently changed into completely different cell types - such as nerve cells, for example. This can be done entirely without stem cells.
Jul 31st, 2013
Read more