A flip of the mitotic spindle has disastrous consequences for epithelial cells
Scientists use genetics and live cell imaging to illuminate molecular mechanisms that position the cell division machinery in growing tissues.
Jul 21st, 2013
Read more
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Scientists use genetics and live cell imaging to illuminate molecular mechanisms that position the cell division machinery in growing tissues.
Jul 21st, 2013
Read more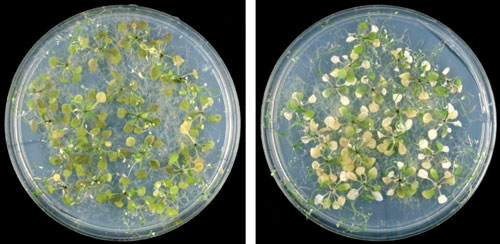 Tolerance of phosphorus limitation in plants is linked to a previously unidentified lipid family.
Tolerance of phosphorus limitation in plants is linked to a previously unidentified lipid family.
Jul 19th, 2013
Read more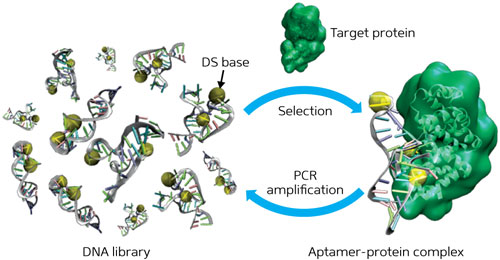 An artificial base that enhances the protein-binding affinity and selectivity of DNA expands the DNA machinery.
An artificial base that enhances the protein-binding affinity and selectivity of DNA expands the DNA machinery.
Jul 19th, 2013
Read more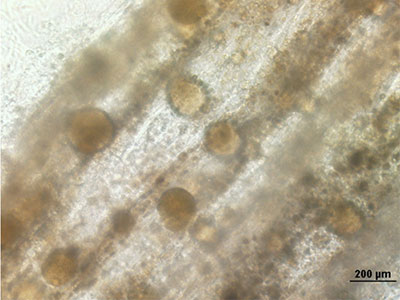 Hair loss is a common disorder that affects many men and women due to aging or medical conditions. Current FDA-approved drugs can minimize further hair loss but are unable to regrow new hair. The Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN) has recently engineered a new hair follicle model that could help discover new drugs for hair regeneration.
Hair loss is a common disorder that affects many men and women due to aging or medical conditions. Current FDA-approved drugs can minimize further hair loss but are unable to regrow new hair. The Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN) has recently engineered a new hair follicle model that could help discover new drugs for hair regeneration.
Jul 19th, 2013
Read more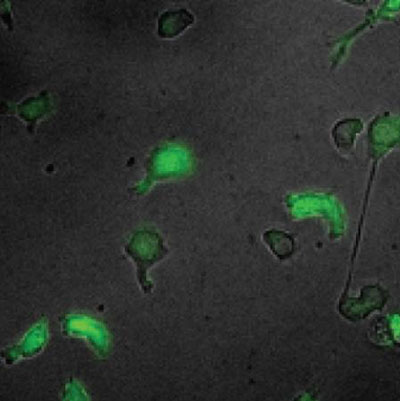 Biologists at the Caltech have worked out the details of a mechanism that leads undifferentiated blood stem cells to become macrophages - immune cells that attack bacteria and other foreign pathogens. The process involves an unexpected cycle in which cell division slows, leading to an increased accumulation of a particular regulatory protein that in turn slows cell division further. The finding provides new insight into how stem cells are guided to generate one cell type as opposed to another.
Biologists at the Caltech have worked out the details of a mechanism that leads undifferentiated blood stem cells to become macrophages - immune cells that attack bacteria and other foreign pathogens. The process involves an unexpected cycle in which cell division slows, leading to an increased accumulation of a particular regulatory protein that in turn slows cell division further. The finding provides new insight into how stem cells are guided to generate one cell type as opposed to another.
Jul 18th, 2013
Read more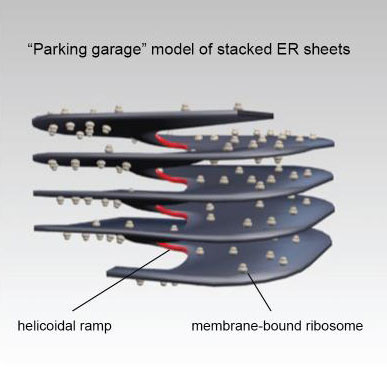 Researchers have refined a new microscopy imaging method to visualize exactly how the endoplasmic reticulum sheets are stacked, revealing that the 3D structure of the sheets resembles a parking garage with helical ramps connecting the different levels.
Researchers have refined a new microscopy imaging method to visualize exactly how the endoplasmic reticulum sheets are stacked, revealing that the 3D structure of the sheets resembles a parking garage with helical ramps connecting the different levels.
Jul 18th, 2013
Read more The search for new drugs, including those for cancer, is set to speed up thanks to a new research technique invented by scientists at the Nanyang Technological University.
The search for new drugs, including those for cancer, is set to speed up thanks to a new research technique invented by scientists at the Nanyang Technological University.
Jul 18th, 2013
Read more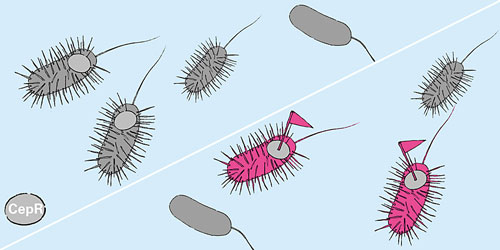 Researchers at the University of Basel have developed a live-cell fluorescent labeling that makes bacterial cell-to-cell communication pathways visible. The communication between bacterial cells is essential in the regulation of processes within bacterial populations, such as biofilm development.
Researchers at the University of Basel have developed a live-cell fluorescent labeling that makes bacterial cell-to-cell communication pathways visible. The communication between bacterial cells is essential in the regulation of processes within bacterial populations, such as biofilm development.
Jul 18th, 2013
Read more Granada-based researchers patent a new biomaterial based on an activated carbon cloth support that acts as scaffolding for the construction of cells capable of bone regeneration.
Granada-based researchers patent a new biomaterial based on an activated carbon cloth support that acts as scaffolding for the construction of cells capable of bone regeneration.
Jul 18th, 2013
Read more Michael Laub studies the complex interactions that underlie cells' responses to their environment.
Michael Laub studies the complex interactions that underlie cells' responses to their environment.
Jul 18th, 2013
Read more Engineered liver tissue developed at MIT could help scientists test new drugs and vaccines.
Engineered liver tissue developed at MIT could help scientists test new drugs and vaccines.
Jul 18th, 2013
Read moreHow to cure malignant brain tumour? Why two cells from the same organism, in spite of having identical gene set up, have different shape and functions? How small variations in human genes determine changes in the way we think, feel and behave? Answers to such questions are sought by scientists from the new Laboratory of Molecular Neurobiology of the Nencki Institute.
Jul 18th, 2013
Read more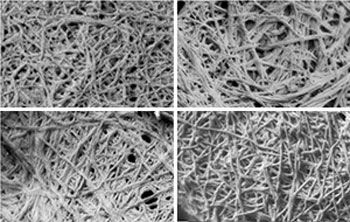 Insight into the mechanism of protein aggregation provides a model system that could lead to treatments for several associated diseases.
Insight into the mechanism of protein aggregation provides a model system that could lead to treatments for several associated diseases.
Jul 17th, 2013
Read more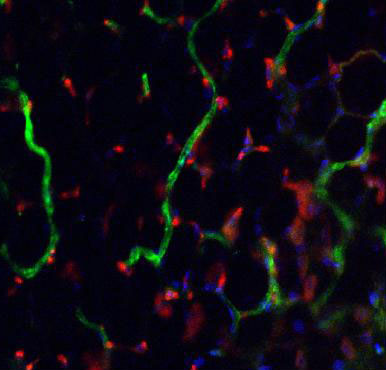 Researchers at Johns Hopkins have coaxed stem cells into forming networks of new blood vessels in the laboratory, then successfully transplanted them into mice. The stem cells are made by reprogramming ordinary cells, so the new technique could potentially be used to make blood vessels genetically matched to individual patients and unlikely to be rejected by their immune systems, the investigators say.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins have coaxed stem cells into forming networks of new blood vessels in the laboratory, then successfully transplanted them into mice. The stem cells are made by reprogramming ordinary cells, so the new technique could potentially be used to make blood vessels genetically matched to individual patients and unlikely to be rejected by their immune systems, the investigators say.
Jul 16th, 2013
Read more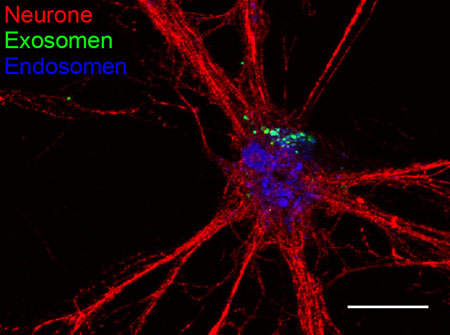 Glial cells send 'care packages' including protective proteins and genetic information to nerve cells.
Glial cells send 'care packages' including protective proteins and genetic information to nerve cells.
Jul 16th, 2013
Read moreNew research provides a rare 'picture' of the activity taking place at the single molecular level: visual evidence of the mechanisms involved when a cell transports mRNA (or messenger RNA) to where a protein is needed to perform a cellular function.
Jul 15th, 2013
Read moreImagine millions of jigsaw puzzle pieces scattered across a football field, with too few people and too little time available to assemble the picture. Scientists in the new but fast-growing field of computational genomics are facing a similar dilemma.
Jul 15th, 2013
Read more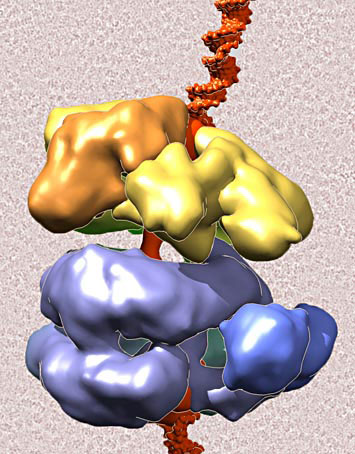 Scientists have captured new details of the biochemical interactions necessary for cell division -- molecular images showing how the enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix gets drawn to and wrapped around its target. The research may suggest ways for stopping cell division when it goes awry.
Scientists have captured new details of the biochemical interactions necessary for cell division -- molecular images showing how the enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix gets drawn to and wrapped around its target. The research may suggest ways for stopping cell division when it goes awry.
Jul 14th, 2013
Read more