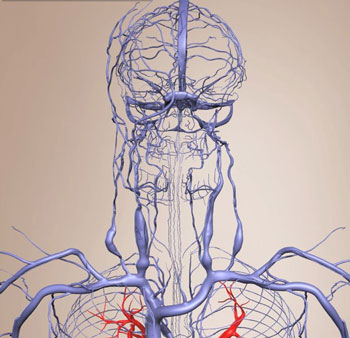
 Researchers have known for some time that the blood vessels that transport blood to and from tissues and organs in the body are more than just bodily pipelines. Arterioles and capillaries, the small vessels, actually play a key role in regulating the flow of the blood they're carrying. Biomedical engineers at Drexel University, who study cardiovascular function, are creating a mathematical model that explains just how they do it.
Researchers have known for some time that the blood vessels that transport blood to and from tissues and organs in the body are more than just bodily pipelines. Arterioles and capillaries, the small vessels, actually play a key role in regulating the flow of the blood they're carrying. Biomedical engineers at Drexel University, who study cardiovascular function, are creating a mathematical model that explains just how they do it.
Sep 4th, 2013
Read more
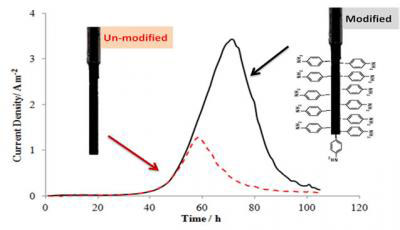 A team of researchers have found evidence that altering the chemistry of an electrode surface can help microbial communities to connect to the electrode to produce more electricity more rapidly compared to unmodified electrodes. Practical applications of these systems include current generation, wastewater treatment, and biochemical and biofuel production.
A team of researchers have found evidence that altering the chemistry of an electrode surface can help microbial communities to connect to the electrode to produce more electricity more rapidly compared to unmodified electrodes. Practical applications of these systems include current generation, wastewater treatment, and biochemical and biofuel production.
Sep 4th, 2013
Read more
New method for turning genes on and off could enable more complex synthetic biology circuits.
Sep 3rd, 2013
Read more
The SeaBioTech project, started in 2012, is intended to close some of these knowledge gaps by looking in the seas and oceans around the globe for life forms with novel properties. The aim is to find raw material for the world's biotechnology industry, with a particular emphasis on antibiotics and other medical compounds.
Sep 2nd, 2013
Read more
 Demystifying the chemical processes that create a wine's aroma, and the invaluable potential application of that understanding in winemaking, is the new objective of scientists in Uruguay who, with European partners, also recently sequenced the genome of the high-value Tannat grape, from which 'the most healthy of red wines' are fermented.
Demystifying the chemical processes that create a wine's aroma, and the invaluable potential application of that understanding in winemaking, is the new objective of scientists in Uruguay who, with European partners, also recently sequenced the genome of the high-value Tannat grape, from which 'the most healthy of red wines' are fermented.
Sep 2nd, 2013
Read more
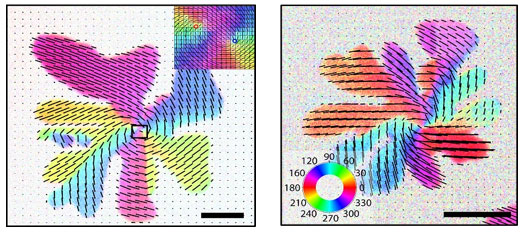 Biological cells are surrounded by a membrane, and here some of the most important processes for sustaining life take place. There can also be something very beautiful happening in membranes, researchers from the University of Southern Denmark have discovered: Membranes can contain beautiful, mysterious patterns.
Biological cells are surrounded by a membrane, and here some of the most important processes for sustaining life take place. There can also be something very beautiful happening in membranes, researchers from the University of Southern Denmark have discovered: Membranes can contain beautiful, mysterious patterns.
Aug 30th, 2013
Read more
 Research on new polymer additives that enhance the ability of orally administered drugs will result in greater effectiveness and fewer side effects.
Research on new polymer additives that enhance the ability of orally administered drugs will result in greater effectiveness and fewer side effects.
Aug 28th, 2013
Read more
University of Washington researchers have performed what they believe is the first noninvasive human-to-human brain interface, with one researcher able to send a brain signal via the Internet to control the hand motions of a fellow researcher.
Aug 27th, 2013
Read more
Scientists at the Scripps Research Institute have found a way to apply a powerful new DNA-editing technology more broadly than ever before.
Aug 26th, 2013
Read more
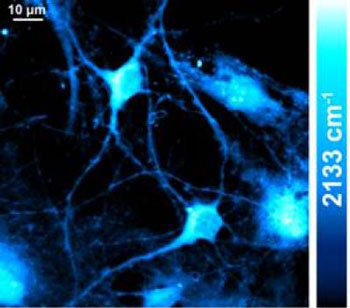 Columbia researchers make significant step in understanding and imaging protein synthesis.
Columbia researchers make significant step in understanding and imaging protein synthesis.
Aug 26th, 2013
Read more
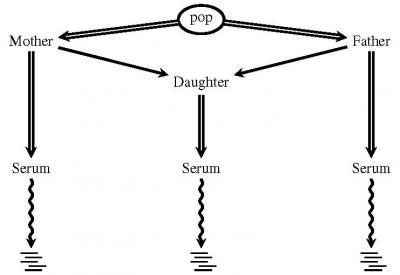 Researchers report on a new software tool known as DeNovoGear, which uses statistical probabilities to help identify mutations and more accurately pinpoint their source and their possible significance for health.
Researchers report on a new software tool known as DeNovoGear, which uses statistical probabilities to help identify mutations and more accurately pinpoint their source and their possible significance for health.
Aug 26th, 2013
Read more
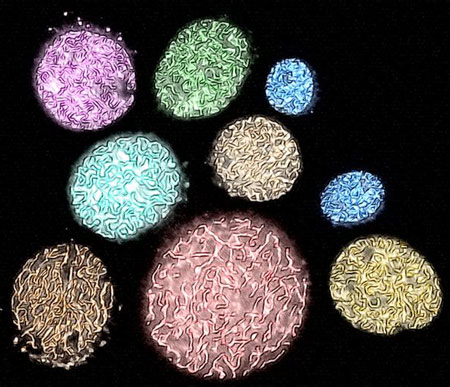 Scientists at the Research Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP) found that the structure of Chromosomes is supported by a kind of molecular skeleton, made of cohesin.
Scientists at the Research Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP) found that the structure of Chromosomes is supported by a kind of molecular skeleton, made of cohesin.
Aug 26th, 2013
Read more
In an era of widespread genetic sequencing, the ability to edit and alter an organism's DNA is a powerful way to explore the information within and how it guides biological function.
Aug 23rd, 2013
Read more
Research has discovered that combinations of bacteria commonly found in water pipes can form a biofilm which enables other potentially more harmful bacteria to thrive.
Aug 22nd, 2013
Read more
Understanding protein function on a genomic scale is now one of the central goals of biology. The project ENZYME MICROARRAYS ('An integrated technology for the deconvolution of complex biochemical systems, drug discovery and diagnostics') was aimed at developing new techniques to help better understand protein functioning.
Aug 20th, 2013
Read more
 Biologist Peter Reddien seeks to understand planarians' famous ability to grow new body parts.
Biologist Peter Reddien seeks to understand planarians' famous ability to grow new body parts.
Aug 20th, 2013
Read more
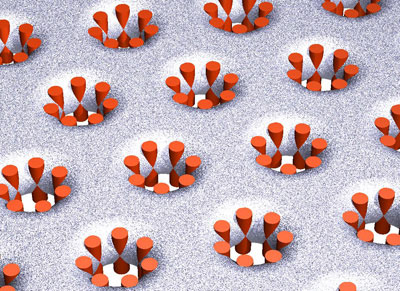 A new study by Rice University biophysicists offers the most comprehensive picture yet of the molecular-level action of melittin, the principal toxin in bee venom. The research could aid in the development of new drugs that use a similar mechanism as melittin's to attack cancer and bacteria.
A new study by Rice University biophysicists offers the most comprehensive picture yet of the molecular-level action of melittin, the principal toxin in bee venom. The research could aid in the development of new drugs that use a similar mechanism as melittin's to attack cancer and bacteria.
Aug 18th, 2013
Read more
 Hyperswarming, pathogenic bacteria have repeatedly evolved in a lab, and the good news is that they should be less of a problem to us than their less mobile kin. That's because those hyperswarmers, adorned with multiple whipping flagella, are also much worse at sticking together on surfaces in hard-to-treat biofilms. They might even help us figure out a way to develop anti-biofilm therapies for use in people with cystic fibrosis or other conditions.
Hyperswarming, pathogenic bacteria have repeatedly evolved in a lab, and the good news is that they should be less of a problem to us than their less mobile kin. That's because those hyperswarmers, adorned with multiple whipping flagella, are also much worse at sticking together on surfaces in hard-to-treat biofilms. They might even help us figure out a way to develop anti-biofilm therapies for use in people with cystic fibrosis or other conditions.
Aug 15th, 2013
Read more
 Researchers have known for some time that the blood vessels that transport blood to and from tissues and organs in the body are more than just bodily pipelines. Arterioles and capillaries, the small vessels, actually play a key role in regulating the flow of the blood they're carrying. Biomedical engineers at Drexel University, who study cardiovascular function, are creating a mathematical model that explains just how they do it.
Researchers have known for some time that the blood vessels that transport blood to and from tissues and organs in the body are more than just bodily pipelines. Arterioles and capillaries, the small vessels, actually play a key role in regulating the flow of the blood they're carrying. Biomedical engineers at Drexel University, who study cardiovascular function, are creating a mathematical model that explains just how they do it.
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed








