Researchers say they have identified certain proteins that play a key role in controlling pluripotency, which may mean a potential breakthrough in producing these cells.
Jul 5th, 2013
Read more
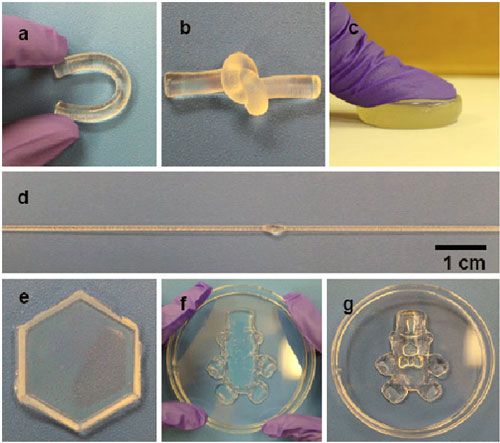 There is growing research of hydrogels, the gelatinous substance that, because of its toughness and plasticity, has several biomedical applications, including cartilage repair, implants for minimally invasive surgery and drug delivery.
There is growing research of hydrogels, the gelatinous substance that, because of its toughness and plasticity, has several biomedical applications, including cartilage repair, implants for minimally invasive surgery and drug delivery.
Jul 5th, 2013
Read more
A sensitive technique for taking the RNA inventory of individual cells offers researchers a powerful tool for exploring cellular biology and function.
Jul 5th, 2013
Read more
Researchers have determined that the transcription factor Nanog, which plays a critical role in the self-renewal of embryonic stem cells, is expressed in a manner similar to other pluripotency markers. This finding contradicts the field's presumptions about this important gene and its role in the differentiation of embryonic stem cells.
Jul 3rd, 2013
Read more
An approach that directly inserts proteins into polymer-based cell membranes improves drug-screening platforms.
Jul 3rd, 2013
Read more
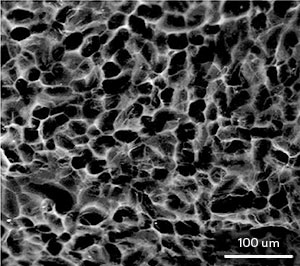 When injected as a hydrogel rather than in solution, an anticancer protein treats liver tumors more effectively.
When injected as a hydrogel rather than in solution, an anticancer protein treats liver tumors more effectively.
Jul 3rd, 2013
Read more
Transport proteins are responsible for moving materials such as nutrients and metabolic products through a cell's outer membrane, which seals and protects all living cells, to the cell's interior. A team has now developed a groundbreaking new way to measure the activity of transporter proteins in living organisms.
Jul 2nd, 2013
Read more
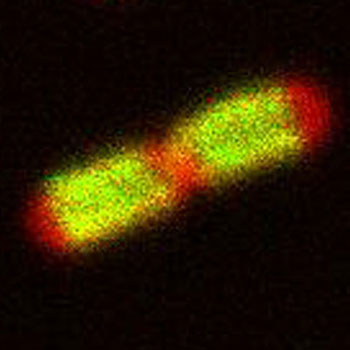
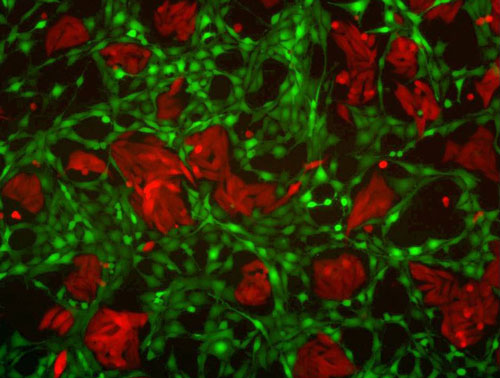 University of T�bingen researchers help develop a way to trace communication between cells.
University of T�bingen researchers help develop a way to trace communication between cells.
Jul 2nd, 2013
Read more
Scientists have discovered a molecular network in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) that integrates cell communication signals to keep the cell in its stem cell state.
Jul 2nd, 2013
Read more
Knowing virtually everything about how the body's cells make transitions from one state to another - for instance, precisely how particular cells develop into multi-cellular organisms - would be a major jump forward in understanding the basics of what drives biological processes.
Jul 1st, 2013
Read more
 A new study has discovered the role of a protein in bacteria that cause a wide variety of diseases, including typhoid fever, plague, meningitis and dysentery. The results may lead to new and improved antibiotics for humans and animals.
A new study has discovered the role of a protein in bacteria that cause a wide variety of diseases, including typhoid fever, plague, meningitis and dysentery. The results may lead to new and improved antibiotics for humans and animals.
Jul 1st, 2013
Read more
Synthetic biology technology could lead to new antibiotics, modified protein-generators.
Jun 29th, 2013
Read more
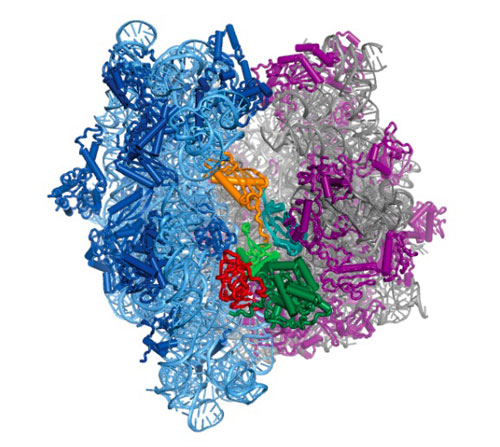 Berkeley Lab scientists create atomic-scale structure of ribosome attached to a molecule that controls its motion.
Berkeley Lab scientists create atomic-scale structure of ribosome attached to a molecule that controls its motion.
Jun 29th, 2013
Read more
Scientists using sophisticated imaging techniques have observed a molecular protein folding process that may help medical researchers understand and treat diseases such as Alzheimer's, Lou Gehrig's and cancer.
Jun 28th, 2013
Read more
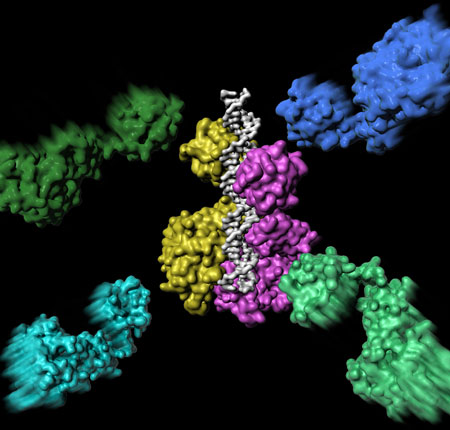 New studies detail breakthroughs in his research on protein-DNA recognition. The findings may have profound implications for furthering research into cancer and other genetically based diseases.
New studies detail breakthroughs in his research on protein-DNA recognition. The findings may have profound implications for furthering research into cancer and other genetically based diseases.
Jun 28th, 2013
Read more
CEA-Leti today introduced a new video lens-free imaging technique that redefines bio imaging, provides significant advantages over traditional microscopy, and opens a new range of capabilities for researchers, such as real-time monitoring of cell cultures.
Jun 26th, 2013
Read more
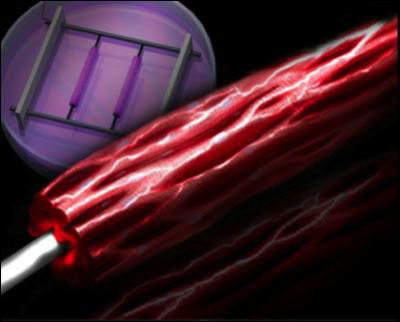 A new method of maturing human heart cells that simulates the natural growth environment of heart cells while applying electrical pulses to mimic the heart rate of fetal humans has led researchers at the University of Toronto to an electrifying step forward for cardiac research.
A new method of maturing human heart cells that simulates the natural growth environment of heart cells while applying electrical pulses to mimic the heart rate of fetal humans has led researchers at the University of Toronto to an electrifying step forward for cardiac research.
Jun 24th, 2013
Read more
Biologists reveal how cells control the direction in which the genome is read.
Jun 24th, 2013
Read more

 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed





