Showing Spotlights 657 - 664 of 2879 in category All (newest first):
 Researchers commonly observe a relative rotation between individual layers of 2D materials. Importantly, these interlayer rotation angles, i.e. at what angle two individual layers are oriented towards each other, influence the electronic properties of the resulting material system. In new work, researchers reveal a general moire-driven mechanism that governs the interlayer rotation. At the core of these findings is the concept of the van der Waals dislocation, a term the team uses to describe the commensurability/incommensurability defect in bilayer crystalline materials.
Researchers commonly observe a relative rotation between individual layers of 2D materials. Importantly, these interlayer rotation angles, i.e. at what angle two individual layers are oriented towards each other, influence the electronic properties of the resulting material system. In new work, researchers reveal a general moire-driven mechanism that governs the interlayer rotation. At the core of these findings is the concept of the van der Waals dislocation, a term the team uses to describe the commensurability/incommensurability defect in bilayer crystalline materials.
May 31st, 2019
 The use of TiO2 nanoparticles activated by light and ultrasound has been studied extensively for cancer treatments. For the first time, researchers have shown the nanoparticles can be effectively activated by microwaves for cancer cell destruction - potentially opening new doors for patients fighting cancer. They propose the use of microwaves and TiO2 nanoparticles to induce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which has the potential to be a safer, more effective modality for cancer treatment.
The use of TiO2 nanoparticles activated by light and ultrasound has been studied extensively for cancer treatments. For the first time, researchers have shown the nanoparticles can be effectively activated by microwaves for cancer cell destruction - potentially opening new doors for patients fighting cancer. They propose the use of microwaves and TiO2 nanoparticles to induce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which has the potential to be a safer, more effective modality for cancer treatment.
May 30th, 2019
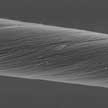 Carbon nanotube (CNT) fiber is an important one-dimensional macroscopic material. The directional assembly of CNTs can help the fiber realize high mechanical, high electrical and high thermal performance. By introducing thermosetting polymer between the carbon nanotube fibers, the cured polymer can overcome the weak van der Waals interaction between the CNTs and further improve the fiber thermal transport. This results in an effective improvement in thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of CNT fibers.
Carbon nanotube (CNT) fiber is an important one-dimensional macroscopic material. The directional assembly of CNTs can help the fiber realize high mechanical, high electrical and high thermal performance. By introducing thermosetting polymer between the carbon nanotube fibers, the cured polymer can overcome the weak van der Waals interaction between the CNTs and further improve the fiber thermal transport. This results in an effective improvement in thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of CNT fibers.
May 21st, 2019
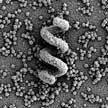 By applying concepts developed in micro- and nanorobotics, researchers demonstrate the controlled motion and delivery of cargo payloads embedded in metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). The helical MOF-based micromachine, propelled by artificial bacterial flagella, can swim and follow complex trajectories in three dimensions under the control of weak rotational magnetic fields. These swimmers are tumor-responsiv and can act as selectively automated and targeted drug delivery platforms.
By applying concepts developed in micro- and nanorobotics, researchers demonstrate the controlled motion and delivery of cargo payloads embedded in metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). The helical MOF-based micromachine, propelled by artificial bacterial flagella, can swim and follow complex trajectories in three dimensions under the control of weak rotational magnetic fields. These swimmers are tumor-responsiv and can act as selectively automated and targeted drug delivery platforms.
May 20th, 2019
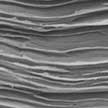 Graphene's outstanding mechanical and electrical properties make it a very attractive material for applications in aerospace and flexible electronics. This, however, requires the assembly of graphene into macroscopic graphene nanocomposites. Researchers report a novel strategy to 'stitch' reduced graphene oxide nanosheets into ultra-strong, super tough, and highly conductive graphene films using only small amounts of cross-linker. Their technique provides substantial improvement in multiple properties including tensile strength, toughness, electrical conductivity, EMI shielding capability, and resistance to mechanical damage.
Graphene's outstanding mechanical and electrical properties make it a very attractive material for applications in aerospace and flexible electronics. This, however, requires the assembly of graphene into macroscopic graphene nanocomposites. Researchers report a novel strategy to 'stitch' reduced graphene oxide nanosheets into ultra-strong, super tough, and highly conductive graphene films using only small amounts of cross-linker. Their technique provides substantial improvement in multiple properties including tensile strength, toughness, electrical conductivity, EMI shielding capability, and resistance to mechanical damage.
May 17th, 2019
 Researchers have developed a comprehensive approach involving simple and facile steps to fabricate a wearable energy storage device based on carbon nanotube coated cotton yarn. All device components are flexible. According to the team, this is the first device that has been proven to be stable under rigorous washing conditions in the presence of hot water, detergents and high torque (spinning action of washing machine). This provides the device with comprehensive mechanical stability.
Researchers have developed a comprehensive approach involving simple and facile steps to fabricate a wearable energy storage device based on carbon nanotube coated cotton yarn. All device components are flexible. According to the team, this is the first device that has been proven to be stable under rigorous washing conditions in the presence of hot water, detergents and high torque (spinning action of washing machine). This provides the device with comprehensive mechanical stability.
May 15th, 2019
 Borophene, the atomically flat form of boron, differs from graphene and other two-dimensional (2D) materials in an important way: It can't be reduced from a larger natural form because bulk boron is not naturally layered. While graphite is composed of stacks of atomically thin sheets that can be peeled off one at a time to make graphene, there is no such analogous process for making 2D boron. Or so researchers had thought. Now, however, researchers have synthesized free-standing borophene for the first time and in a scalable manner.
Borophene, the atomically flat form of boron, differs from graphene and other two-dimensional (2D) materials in an important way: It can't be reduced from a larger natural form because bulk boron is not naturally layered. While graphite is composed of stacks of atomically thin sheets that can be peeled off one at a time to make graphene, there is no such analogous process for making 2D boron. Or so researchers had thought. Now, however, researchers have synthesized free-standing borophene for the first time and in a scalable manner.
May 14th, 2019
 Superlubricity is a phenomenon where two surfaces slide over each other with barely any resistance (a state that is called near-zero friction). This is a very special case where friction almost vanishes between two surfaces. The difficulty of achieving superlubricity in mechanical systems is due to the very complex physical, chemical, and mechanical interactions that occur simultaneously at the sliding interfaces of these systems. Superlubricity is one of the most promising properties of functional nanomaterials for energy saving applications.
Superlubricity is a phenomenon where two surfaces slide over each other with barely any resistance (a state that is called near-zero friction). This is a very special case where friction almost vanishes between two surfaces. The difficulty of achieving superlubricity in mechanical systems is due to the very complex physical, chemical, and mechanical interactions that occur simultaneously at the sliding interfaces of these systems. Superlubricity is one of the most promising properties of functional nanomaterials for energy saving applications.
May 10th, 2019
 Researchers commonly observe a relative rotation between individual layers of 2D materials. Importantly, these interlayer rotation angles, i.e. at what angle two individual layers are oriented towards each other, influence the electronic properties of the resulting material system. In new work, researchers reveal a general moire-driven mechanism that governs the interlayer rotation. At the core of these findings is the concept of the van der Waals dislocation, a term the team uses to describe the commensurability/incommensurability defect in bilayer crystalline materials.
Researchers commonly observe a relative rotation between individual layers of 2D materials. Importantly, these interlayer rotation angles, i.e. at what angle two individual layers are oriented towards each other, influence the electronic properties of the resulting material system. In new work, researchers reveal a general moire-driven mechanism that governs the interlayer rotation. At the core of these findings is the concept of the van der Waals dislocation, a term the team uses to describe the commensurability/incommensurability defect in bilayer crystalline materials.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





