Showing Spotlights 561 - 568 of 2879 in category All (newest first):
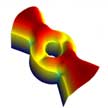 More than 25 years since the discovery of superconductivity in strontium ruthanate (SRO), understanding the properties of this material remains as challenging as ever. Researchers now demonstrated that a SRO sample can allow the two energetically degenerate condensates of Cooper-pairs with opposite momentum to segregate in domains, with a domain wall in between where chirality changes. To use the analogy to Moses parting the sea, here the Red Sea would spontaneously part into 'magenta' and 'yellow' seas on either side.
More than 25 years since the discovery of superconductivity in strontium ruthanate (SRO), understanding the properties of this material remains as challenging as ever. Researchers now demonstrated that a SRO sample can allow the two energetically degenerate condensates of Cooper-pairs with opposite momentum to segregate in domains, with a domain wall in between where chirality changes. To use the analogy to Moses parting the sea, here the Red Sea would spontaneously part into 'magenta' and 'yellow' seas on either side.
May 27th, 2020
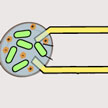 New research demonstrates the integration of synthetic biology with electronic circuitry through engineered population dynamics that regulate the accumulation of charged metabolites. The resulting sensor devices can detect changes in bacterial population in response to the presence of chemicals, light or pH. Connecting bacterial gene expression to electrodes is an appealing approach to interface genetic circuits with microelectronics for multiple applications. In this work, researchers engineered bacterial circuits capable of controlling the conductivity of the media via cell growth and death. Therefore, the electronic output is controlled by a killing gene.
New research demonstrates the integration of synthetic biology with electronic circuitry through engineered population dynamics that regulate the accumulation of charged metabolites. The resulting sensor devices can detect changes in bacterial population in response to the presence of chemicals, light or pH. Connecting bacterial gene expression to electrodes is an appealing approach to interface genetic circuits with microelectronics for multiple applications. In this work, researchers engineered bacterial circuits capable of controlling the conductivity of the media via cell growth and death. Therefore, the electronic output is controlled by a killing gene.
May 26th, 2020
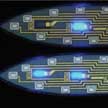 Miniaturized needle-like carriers in high aspect ratio structures are a novel class of implantable electronic devices. They are used to deliver tiny sensors and stimulation tools inside the body via minimally invasive injection or insertion into a specific area of an organ. A recent review summarizes the latest developments in materials, designs, and manufacturing techniques in the field of injectable biomedical devices, highlighting unique applications and demonstrations of viable clinical tools that were applied in various internal organs.
Miniaturized needle-like carriers in high aspect ratio structures are a novel class of implantable electronic devices. They are used to deliver tiny sensors and stimulation tools inside the body via minimally invasive injection or insertion into a specific area of an organ. A recent review summarizes the latest developments in materials, designs, and manufacturing techniques in the field of injectable biomedical devices, highlighting unique applications and demonstrations of viable clinical tools that were applied in various internal organs.
May 19th, 2020
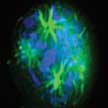 Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is is the most common type of primary liver cancer and one of the most aggressive and hyper-vascularized forms of cancer. Many current chemotherapeutics fail to achieve the effective therapeutic index in the solid tumours due to poor drug penetration, poor bioavailability, non-specificity and drug resistance - a challenging aspect in this field. In search of new modalities, researchers have developed multifunctional polymeric nanoparticles against HCC. These biocompatible multifunctional polymeric nanoparticles hold trimodal affinity towards targeting microtubules, tyrosine kinases, and high-sensitivity imaging system quantum dots.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is is the most common type of primary liver cancer and one of the most aggressive and hyper-vascularized forms of cancer. Many current chemotherapeutics fail to achieve the effective therapeutic index in the solid tumours due to poor drug penetration, poor bioavailability, non-specificity and drug resistance - a challenging aspect in this field. In search of new modalities, researchers have developed multifunctional polymeric nanoparticles against HCC. These biocompatible multifunctional polymeric nanoparticles hold trimodal affinity towards targeting microtubules, tyrosine kinases, and high-sensitivity imaging system quantum dots.
May 14th, 2020
 Breath is one of the main sources of human health parameters that can be used for predicting the state of internal organs. Exhaled breath composition is very complex and the existence of disease marker molecules can be as low as one part per million. That means that using breath for health monitoring purposes requires highly sensitive tools with a recognition ability down to single molecules. Researchers developed a method for fast, on-site and still accurate breath analysis that does not need special preparation of breath samples. The method is based on an electronic nose platform that uses a set of single-walled carbon nanotube sensors deposited on flexible substrates and modified by different semiconducting organic molecules.
Breath is one of the main sources of human health parameters that can be used for predicting the state of internal organs. Exhaled breath composition is very complex and the existence of disease marker molecules can be as low as one part per million. That means that using breath for health monitoring purposes requires highly sensitive tools with a recognition ability down to single molecules. Researchers developed a method for fast, on-site and still accurate breath analysis that does not need special preparation of breath samples. The method is based on an electronic nose platform that uses a set of single-walled carbon nanotube sensors deposited on flexible substrates and modified by different semiconducting organic molecules.
May 13th, 2020
 In the absence of vaccines, many scientists argue that the best approach to control the spread of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) would be fast, cheap, reliable, and portable means of diagnosing COVID-19 infection. In particular, the identification of patients with the highest risk of COVID-19 mortality (i.e. those with co-morbidities such as cardiovascular disorders or massive alveolar damage and progressive respiratory failure) could significantly improve the capacity of healthcare providers to take early action and minimize the possibility of overwhelming care centers, which in turn would save many lives.
In the absence of vaccines, many scientists argue that the best approach to control the spread of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) would be fast, cheap, reliable, and portable means of diagnosing COVID-19 infection. In particular, the identification of patients with the highest risk of COVID-19 mortality (i.e. those with co-morbidities such as cardiovascular disorders or massive alveolar damage and progressive respiratory failure) could significantly improve the capacity of healthcare providers to take early action and minimize the possibility of overwhelming care centers, which in turn would save many lives.
May 12th, 2020
 Researchers exploited for the first time cellular self-recognition process for targeting glioblastoma cells with boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs), a biocompatible, yet inorganic, nanomaterial.
The team loaded the BNNTs with doxorubicin, a powerful chemotherapy drug, and then functionalized them with glioblastoma cell membranes This targeting approach benefits from the ability of cancer cells to recognize each other due to similarities present on their membrane that make them different from healthy cells.
Researchers exploited for the first time cellular self-recognition process for targeting glioblastoma cells with boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs), a biocompatible, yet inorganic, nanomaterial.
The team loaded the BNNTs with doxorubicin, a powerful chemotherapy drug, and then functionalized them with glioblastoma cell membranes This targeting approach benefits from the ability of cancer cells to recognize each other due to similarities present on their membrane that make them different from healthy cells.
May 11th, 2020
 Superconducting materials, which entirely lose their electrical resistance at low temperatures, have become ever more widespread over recent years. Nevertheless, the fascinating phenomenon of superconductivity does not cease to surprise, as the kinds of materials able to superconduct, as well as the mechanisms through which superconductivity emerges, have become increasingly diverse. One of the prime examples is found in the compound 2D material tantalum disulfide, where the critical temperature below which superconductivity appears increases multifold as the crystal is made thinner down to a monolayer.
Superconducting materials, which entirely lose their electrical resistance at low temperatures, have become ever more widespread over recent years. Nevertheless, the fascinating phenomenon of superconductivity does not cease to surprise, as the kinds of materials able to superconduct, as well as the mechanisms through which superconductivity emerges, have become increasingly diverse. One of the prime examples is found in the compound 2D material tantalum disulfide, where the critical temperature below which superconductivity appears increases multifold as the crystal is made thinner down to a monolayer.
May 8th, 2020
 More than 25 years since the discovery of superconductivity in strontium ruthanate (SRO), understanding the properties of this material remains as challenging as ever. Researchers now demonstrated that a SRO sample can allow the two energetically degenerate condensates of Cooper-pairs with opposite momentum to segregate in domains, with a domain wall in between where chirality changes. To use the analogy to Moses parting the sea, here the Red Sea would spontaneously part into 'magenta' and 'yellow' seas on either side.
More than 25 years since the discovery of superconductivity in strontium ruthanate (SRO), understanding the properties of this material remains as challenging as ever. Researchers now demonstrated that a SRO sample can allow the two energetically degenerate condensates of Cooper-pairs with opposite momentum to segregate in domains, with a domain wall in between where chirality changes. To use the analogy to Moses parting the sea, here the Red Sea would spontaneously part into 'magenta' and 'yellow' seas on either side.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





