Showing Spotlights 2705 - 2712 of 2851 in category All (newest first):
 Colloidal crystals constructed by monodispersed microspheres packed in ordered arrays represent a new class of advanced materials that are useful in many areas. For example, due to their novel light diffraction and photonic bandgap properties, colloidal crystals are promising elements in the fabrication of devices such as optical filters and switches, chemical and biochemical sensors, and photonic chips. Various self-assembly techniques have been developed to form colloidal crystals on different substrates, including the flow-cell methods, vertical deposition, micromolding in capillaries and so on. Although existing methods can provide colloidal crystals of different structures and quality, efficient approaches to high stability and large scale colloidal crystals are increasingly attracting attention. Generating ordered microstructures in the colloidal crystal films and colloidal crystals with different structures and configurations are particularly important in the fabrication of optical devices.
Colloidal crystals constructed by monodispersed microspheres packed in ordered arrays represent a new class of advanced materials that are useful in many areas. For example, due to their novel light diffraction and photonic bandgap properties, colloidal crystals are promising elements in the fabrication of devices such as optical filters and switches, chemical and biochemical sensors, and photonic chips. Various self-assembly techniques have been developed to form colloidal crystals on different substrates, including the flow-cell methods, vertical deposition, micromolding in capillaries and so on. Although existing methods can provide colloidal crystals of different structures and quality, efficient approaches to high stability and large scale colloidal crystals are increasingly attracting attention. Generating ordered microstructures in the colloidal crystal films and colloidal crystals with different structures and configurations are particularly important in the fabrication of optical devices.
Sep 8th, 2006
 While growth processes of nanostructures are well understood, the stability of artificial nanostructures has not been thoroughly investigated. Fully understanding the fluctuations of nanostructures and their interactions with their surroundings is essential in order to achieve complete shape control of nanostructures. In recent work, French scientists address the morphogenesis, instability and catastrophic collapse of nanostructures.
While growth processes of nanostructures are well understood, the stability of artificial nanostructures has not been thoroughly investigated. Fully understanding the fluctuations of nanostructures and their interactions with their surroundings is essential in order to achieve complete shape control of nanostructures. In recent work, French scientists address the morphogenesis, instability and catastrophic collapse of nanostructures.
Sep 7th, 2006
 Nanocrystal engineering learned from biominerals holds promises for the development in biology, chemistry, and materials science. Biominerals have inspired novel bottom-up approaches to the development of functional materials for some time now. The morphology, crystallographic orientation, incorporated organic molecules, and emergent properties of carbonate-based biominerals already have been demonstrated. Typical examples of these biominerals are certain layers of seashells, corals, and eggshells. New research now clarifies that biominerals are oriented architectures of calcium carbonate nanocrystals 20?100 nm in size with incorporation of biopolymers.
Nanocrystal engineering learned from biominerals holds promises for the development in biology, chemistry, and materials science. Biominerals have inspired novel bottom-up approaches to the development of functional materials for some time now. The morphology, crystallographic orientation, incorporated organic molecules, and emergent properties of carbonate-based biominerals already have been demonstrated. Typical examples of these biominerals are certain layers of seashells, corals, and eggshells. New research now clarifies that biominerals are oriented architectures of calcium carbonate nanocrystals 20?100 nm in size with incorporation of biopolymers.
Sep 6th, 2006
 These days we are debating if nanoparticles in sunblock and toothpaste are safe. The ancient Greeks and Romans didn't know about such things - but they already used nanotechnology in their cosmetics. A group of researchers in France showed that lead-based chemistry, which was initiated in Egypt more than 4000 years ago, could result in the synthesis of lead sulfide (PbS, galena) nanocrystals. With a diameter of about 5 nm, the appearance of these crystals is quite similar to PbS quantum dots synthesized by modern materials science techniques.
These days we are debating if nanoparticles in sunblock and toothpaste are safe. The ancient Greeks and Romans didn't know about such things - but they already used nanotechnology in their cosmetics. A group of researchers in France showed that lead-based chemistry, which was initiated in Egypt more than 4000 years ago, could result in the synthesis of lead sulfide (PbS, galena) nanocrystals. With a diameter of about 5 nm, the appearance of these crystals is quite similar to PbS quantum dots synthesized by modern materials science techniques.
Sep 5th, 2006
 Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are considered the most promising material for field emitters and a practical example are CNTs as electron emitters for field emission displays (FED). CNT emitters are generally fabricated by indirect growth methods such as screen-printing and electrophoresis. These methods show advantages in lowering the coating temperature and scale-up of the substrate size, but the direction of CNTs cannot be well controlled and a post-treatment process is generally necessary to enhance the performance of CNT emitters. In contrast to the indirect method, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a common technique for growing nanotubes directly on the substrate with the assistance of metallic catalysts. With the CVD method, CNTs can be grown at desired locations with a specified direction. However,most synthesis technologies such as conventional thermal CVD or plasma enhanced CVD are performed at temperatures over 500 C, which may restrict the application of CNTs on plastic substrates. Therefore, lowering the growth temperature for CNTs is one of the important directions for facilitating CNT applications.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are considered the most promising material for field emitters and a practical example are CNTs as electron emitters for field emission displays (FED). CNT emitters are generally fabricated by indirect growth methods such as screen-printing and electrophoresis. These methods show advantages in lowering the coating temperature and scale-up of the substrate size, but the direction of CNTs cannot be well controlled and a post-treatment process is generally necessary to enhance the performance of CNT emitters. In contrast to the indirect method, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a common technique for growing nanotubes directly on the substrate with the assistance of metallic catalysts. With the CVD method, CNTs can be grown at desired locations with a specified direction. However,most synthesis technologies such as conventional thermal CVD or plasma enhanced CVD are performed at temperatures over 500 C, which may restrict the application of CNTs on plastic substrates. Therefore, lowering the growth temperature for CNTs is one of the important directions for facilitating CNT applications.
Sep 1st, 2006
 Recent developments in DNA-based nanotechnology have shown the suitability of this novel assembly method for constructing useful nanostructures. DNA molecules can serve as precisely controllable and programmable scaffolds for organizing functional nanomaterials in the design, fabrication, and characterization of nanometer scale electronic devices and sensors. DNA-templated metallic nanowires are such an example and over the past few years DNA scaffolds have been metallized with silver, gold, palladium, platinum and copper. DNA-based fabrication methods could ultimately lead to naturally bio-compatible nanodevices.
Recent developments in DNA-based nanotechnology have shown the suitability of this novel assembly method for constructing useful nanostructures. DNA molecules can serve as precisely controllable and programmable scaffolds for organizing functional nanomaterials in the design, fabrication, and characterization of nanometer scale electronic devices and sensors. DNA-templated metallic nanowires are such an example and over the past few years DNA scaffolds have been metallized with silver, gold, palladium, platinum and copper. DNA-based fabrication methods could ultimately lead to naturally bio-compatible nanodevices.
Aug 31st, 2006
 Carbon nanomaterials have been studied as superior sorbents for their potential environmental applications to remove pollutants such as organic pollutants, metals, fluorides and radionuclides. Most of these studies focused on the adsorption process and few dealt with the interfacial interactions of organic contaminants with carbon nanomaterials in aqueous media. However, understanding their desorption behavior as well is critical to evaluating environmental and health impacts of carbon nanomaterials. New research looks at the high adsorption capacity and reversible adsorption of PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), many of which are suspected carcinogens, on CNTs. The findings imply the potential release of PAHs if PAH-adsorbed CNTs are inhaled by animals and humans, leading to a high environmental and public health risk.
Carbon nanomaterials have been studied as superior sorbents for their potential environmental applications to remove pollutants such as organic pollutants, metals, fluorides and radionuclides. Most of these studies focused on the adsorption process and few dealt with the interfacial interactions of organic contaminants with carbon nanomaterials in aqueous media. However, understanding their desorption behavior as well is critical to evaluating environmental and health impacts of carbon nanomaterials. New research looks at the high adsorption capacity and reversible adsorption of PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), many of which are suspected carcinogens, on CNTs. The findings imply the potential release of PAHs if PAH-adsorbed CNTs are inhaled by animals and humans, leading to a high environmental and public health risk.
Aug 30th, 2006
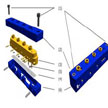 Microscale reactor technology has tremendous advantage over conventional macro-scale or batch chemical processes, and offers versatility for a wide range of applications including chemical analyses, drug discovery, radiotracer synthesis, and the fabrication of engineered nanomaterials. Attention is currently focused on developing scaleable process regimes, using an approach engineers call numbering up. Microreactor technology is defined by a series of interconnected, functionally distinct channels formed on a planar surface, utilizing either hydrodynamic or (EOF) for pumping, with channel dimensions typically between 10-300 microns.
Microscale reactor technology has tremendous advantage over conventional macro-scale or batch chemical processes, and offers versatility for a wide range of applications including chemical analyses, drug discovery, radiotracer synthesis, and the fabrication of engineered nanomaterials. Attention is currently focused on developing scaleable process regimes, using an approach engineers call numbering up. Microreactor technology is defined by a series of interconnected, functionally distinct channels formed on a planar surface, utilizing either hydrodynamic or (EOF) for pumping, with channel dimensions typically between 10-300 microns.
Aug 29th, 2006
 Colloidal crystals constructed by monodispersed microspheres packed in ordered arrays represent a new class of advanced materials that are useful in many areas. For example, due to their novel light diffraction and photonic bandgap properties, colloidal crystals are promising elements in the fabrication of devices such as optical filters and switches, chemical and biochemical sensors, and photonic chips. Various self-assembly techniques have been developed to form colloidal crystals on different substrates, including the flow-cell methods, vertical deposition, micromolding in capillaries and so on. Although existing methods can provide colloidal crystals of different structures and quality, efficient approaches to high stability and large scale colloidal crystals are increasingly attracting attention. Generating ordered microstructures in the colloidal crystal films and colloidal crystals with different structures and configurations are particularly important in the fabrication of optical devices.
Colloidal crystals constructed by monodispersed microspheres packed in ordered arrays represent a new class of advanced materials that are useful in many areas. For example, due to their novel light diffraction and photonic bandgap properties, colloidal crystals are promising elements in the fabrication of devices such as optical filters and switches, chemical and biochemical sensors, and photonic chips. Various self-assembly techniques have been developed to form colloidal crystals on different substrates, including the flow-cell methods, vertical deposition, micromolding in capillaries and so on. Although existing methods can provide colloidal crystals of different structures and quality, efficient approaches to high stability and large scale colloidal crystals are increasingly attracting attention. Generating ordered microstructures in the colloidal crystal films and colloidal crystals with different structures and configurations are particularly important in the fabrication of optical devices.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed