Showing Spotlights 1033 - 1040 of 2876 in category All (newest first):
 Ultrasonics is a promising, non-invasive characterization technique for fluids. The scattering of ultrasound through colloidal suspensions allows determination of accurate particle size distribution, density, and concentration. Controlling these properties enables accurate characterization of nanomedicine drugs and understanding of nanoparticles present in biological systems. Ultrasound is particularly helpful in analyzing optically opaque samples, which have to be heavily diluted in order to be analyzed with optical methods. New work demonstrates for the first time new phenomena in the ultrasonic scattering in nanofluids.
Ultrasonics is a promising, non-invasive characterization technique for fluids. The scattering of ultrasound through colloidal suspensions allows determination of accurate particle size distribution, density, and concentration. Controlling these properties enables accurate characterization of nanomedicine drugs and understanding of nanoparticles present in biological systems. Ultrasound is particularly helpful in analyzing optically opaque samples, which have to be heavily diluted in order to be analyzed with optical methods. New work demonstrates for the first time new phenomena in the ultrasonic scattering in nanofluids.
Apr 15th, 2016
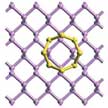 Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries, which employ sulfur as cathode and metallic lithium as anode materials, have been extensively studied as promising alternatives to the widely used lithium-ion batteries because - theoretically - they can render 3-6 times higher energy density. In practice, though, it has proven challenging to approach that theoretical value. Specifically, the rapid capacity fading, low Coulombic efficiency, and irreversible loss of active materials have impeded large-scale commercial use of Li-S batteries. Researchers now have shown that trapping lithium polysulfide species on (nanoscale) host materials is an effective way to overcome these challenges.
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries, which employ sulfur as cathode and metallic lithium as anode materials, have been extensively studied as promising alternatives to the widely used lithium-ion batteries because - theoretically - they can render 3-6 times higher energy density. In practice, though, it has proven challenging to approach that theoretical value. Specifically, the rapid capacity fading, low Coulombic efficiency, and irreversible loss of active materials have impeded large-scale commercial use of Li-S batteries. Researchers now have shown that trapping lithium polysulfide species on (nanoscale) host materials is an effective way to overcome these challenges.
Apr 14th, 2016
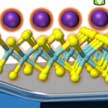 Nanomaterials like graphene and fullerenes provide an excellent platform to enhance weak signals from biomarkers. While graphene and fullerenes perform very well for detecting isolated biomarkers, their ability to amplify emission of biomarkers in a real physiological milieu is limited due to their strong interactions with other biomolecules such as proteins and lipids. A team of researchers now have developed new sensing platforms that use two-dimensional materials beyond graphene.
Nanomaterials like graphene and fullerenes provide an excellent platform to enhance weak signals from biomarkers. While graphene and fullerenes perform very well for detecting isolated biomarkers, their ability to amplify emission of biomarkers in a real physiological milieu is limited due to their strong interactions with other biomolecules such as proteins and lipids. A team of researchers now have developed new sensing platforms that use two-dimensional materials beyond graphene.
Apr 11th, 2016
 In order to make robots and robotic technology more human-like and more human-friendly, smart skin technology is a critical element that helps robots sense the world. These electronic or smart skins could help machines to accurately perceive the environment and better assist human owners. By applying the triboelectric effect and planar electrostatic induction, researchers for the first time have created a self-powered analogue smart skin.
In order to make robots and robotic technology more human-like and more human-friendly, smart skin technology is a critical element that helps robots sense the world. These electronic or smart skins could help machines to accurately perceive the environment and better assist human owners. By applying the triboelectric effect and planar electrostatic induction, researchers for the first time have created a self-powered analogue smart skin.
Apr 8th, 2016
 Modern liquid crystals devices utilize high resistivity liquid crystals characterized by negligibly small concentration of mobile ions. However, these devices are prone to uncontrolled ionic contamination. This contamination can easily happen at any stage of the device fabrication or while operating the device. Ions in liquid crystals can compromise the overall performance of the device by leading to many negative side effects such as image sticking, image flickering, and slow response. Solving these problems requires the development of new methods, suitable for the permanent purification of liquid crystals from ions.
Modern liquid crystals devices utilize high resistivity liquid crystals characterized by negligibly small concentration of mobile ions. However, these devices are prone to uncontrolled ionic contamination. This contamination can easily happen at any stage of the device fabrication or while operating the device. Ions in liquid crystals can compromise the overall performance of the device by leading to many negative side effects such as image sticking, image flickering, and slow response. Solving these problems requires the development of new methods, suitable for the permanent purification of liquid crystals from ions.
Mar 30th, 2016
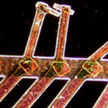 To explore the intrinsic mechanisms of the electrochemical reactions of porous graphene oxide in situ, the single-nanowire electrochemical probe is an effective tool. Although graphene is usually used as an additive in active materials to improve the electrochemical performance, how graphene influences the electrochemical performance and reaction mechanisms of electrode materials is under dispute. To address these issues, researchers have explored single-nanowire electrochemical devices to investigate the capacitance, ion diffusion coefficient, and charge storage mechanisms of graphene.
To explore the intrinsic mechanisms of the electrochemical reactions of porous graphene oxide in situ, the single-nanowire electrochemical probe is an effective tool. Although graphene is usually used as an additive in active materials to improve the electrochemical performance, how graphene influences the electrochemical performance and reaction mechanisms of electrode materials is under dispute. To address these issues, researchers have explored single-nanowire electrochemical devices to investigate the capacitance, ion diffusion coefficient, and charge storage mechanisms of graphene.
Mar 29th, 2016
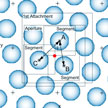 The drawbacks of existing measures for calibrating scanning probe microscopes (SPMs) based on various diffraction gratings and periodic microstructures, are large period and large error of period. Both factors prevent using these measures for precise calibration of SPMs and other instruments operating in the nanometer range. To address this issue, researchers have developed a method of calibration of a scanning probe microscope by lattice constant of a crystal.
The drawbacks of existing measures for calibrating scanning probe microscopes (SPMs) based on various diffraction gratings and periodic microstructures, are large period and large error of period. Both factors prevent using these measures for precise calibration of SPMs and other instruments operating in the nanometer range. To address this issue, researchers have developed a method of calibration of a scanning probe microscope by lattice constant of a crystal.
Mar 25th, 2016
 Lithium (Li) metal-based batteries such as Li-sulfur and Li-air batteries have received considerable attention because Li metal can store 10 times more energy than graphite. However, there are safety and performance concerns for these types of batteries that arise from the formation of dendrites on the electrodes. To address this issue, researchers have proposed an unstacked graphene nanostructured lithium metal anode for lithium metal batteries to inhibit lithium dendrite growth and bring superior electrochemistry performance.
Lithium (Li) metal-based batteries such as Li-sulfur and Li-air batteries have received considerable attention because Li metal can store 10 times more energy than graphite. However, there are safety and performance concerns for these types of batteries that arise from the formation of dendrites on the electrodes. To address this issue, researchers have proposed an unstacked graphene nanostructured lithium metal anode for lithium metal batteries to inhibit lithium dendrite growth and bring superior electrochemistry performance.
Mar 15th, 2016
 Ultrasonics is a promising, non-invasive characterization technique for fluids. The scattering of ultrasound through colloidal suspensions allows determination of accurate particle size distribution, density, and concentration. Controlling these properties enables accurate characterization of nanomedicine drugs and understanding of nanoparticles present in biological systems. Ultrasound is particularly helpful in analyzing optically opaque samples, which have to be heavily diluted in order to be analyzed with optical methods. New work demonstrates for the first time new phenomena in the ultrasonic scattering in nanofluids.
Ultrasonics is a promising, non-invasive characterization technique for fluids. The scattering of ultrasound through colloidal suspensions allows determination of accurate particle size distribution, density, and concentration. Controlling these properties enables accurate characterization of nanomedicine drugs and understanding of nanoparticles present in biological systems. Ultrasound is particularly helpful in analyzing optically opaque samples, which have to be heavily diluted in order to be analyzed with optical methods. New work demonstrates for the first time new phenomena in the ultrasonic scattering in nanofluids.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





