Showing Spotlights 985 - 992 of 2877 in category All (newest first):
 Solar cells absorb incoming sunlight and convert a part of photon energy into electricity. The remainder of photon energy is dissipated as heat. Although the idea is rather counter-intuitive, 'reverse solar cell' systems can also generate electric power by emitting rather than absorbing photons. Such systems - known as thermoradiative cells - generate voltage and electric power via non-equilibrium thermal radiation of infrared photons. Thermoradiative cells offer an opportunity to generate clean energy by harvesting radiation from largely untapped terrestrial thermal emission sources, potentially including the Earth itself.
Solar cells absorb incoming sunlight and convert a part of photon energy into electricity. The remainder of photon energy is dissipated as heat. Although the idea is rather counter-intuitive, 'reverse solar cell' systems can also generate electric power by emitting rather than absorbing photons. Such systems - known as thermoradiative cells - generate voltage and electric power via non-equilibrium thermal radiation of infrared photons. Thermoradiative cells offer an opportunity to generate clean energy by harvesting radiation from largely untapped terrestrial thermal emission sources, potentially including the Earth itself.
Oct 14th, 2016
 Researchers demonstrate for the first time a multifunctional biophotonic platform enabled by the multiband resonance peaks of the plasmonic moire metasurfaces. Benefiting from the multiband nature of moire metasurface and the near-field enhancement from the metal-insulator-metal configuration, the scientists achieved a dual-band metasurface patch with strong plasmonic resonances at both near-infrared and mid-infrared regimes.The plasmonic nanostructures support plasmon resonances at different wavelengths due to the gradient in size and shape.
Researchers demonstrate for the first time a multifunctional biophotonic platform enabled by the multiband resonance peaks of the plasmonic moire metasurfaces. Benefiting from the multiband nature of moire metasurface and the near-field enhancement from the metal-insulator-metal configuration, the scientists achieved a dual-band metasurface patch with strong plasmonic resonances at both near-infrared and mid-infrared regimes.The plasmonic nanostructures support plasmon resonances at different wavelengths due to the gradient in size and shape.
Oct 12th, 2016
 Researchers have explored the role of intrinsic bulk electrical conductivity and surface polarity in the electrocatalysis of polysulfide redox reactions. They synthesized highly porous and conductive titanium carbide (TiC)-based composite cathode materials and to assemble lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries with high sulfur loading. Li-S cells employing the as-synthesized TiC-based cathode exhibited reduced internal resistance, enhanced energy efficiency, and prolonged service life.
Researchers have explored the role of intrinsic bulk electrical conductivity and surface polarity in the electrocatalysis of polysulfide redox reactions. They synthesized highly porous and conductive titanium carbide (TiC)-based composite cathode materials and to assemble lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries with high sulfur loading. Li-S cells employing the as-synthesized TiC-based cathode exhibited reduced internal resistance, enhanced energy efficiency, and prolonged service life.
Oct 10th, 2016
 Microwave hyperthermia is one of the most important clinical thermotherapy techniques due to the instinctive advantages of non-intrusive heating model, fair depth of penetration in tissues and ideal potential of killing tumor cells without surgical risks or toxicity of chemotherapy. Scientists have now developed a novel multifunctional nanoplatform to combine the non-thermal and thermal effects of microwave to achieve enhanced thermal/chemo cancer therapy under mild microwave irradiation.
Microwave hyperthermia is one of the most important clinical thermotherapy techniques due to the instinctive advantages of non-intrusive heating model, fair depth of penetration in tissues and ideal potential of killing tumor cells without surgical risks or toxicity of chemotherapy. Scientists have now developed a novel multifunctional nanoplatform to combine the non-thermal and thermal effects of microwave to achieve enhanced thermal/chemo cancer therapy under mild microwave irradiation.
Oct 7th, 2016
 Carbon nanotube enabled nanocomposites have received much attention as a highly attractive alternative to conventional composite materials due to their mechanical, electrical, thermal, barrier and chemical properties such as electrical conductivity, increased tensile strength, improved heat deflection temperature, or flame retardancy. In new work, researchers report the fabrication of highly conductive carbon nanotube/polylactic acid nanocomposites used as 3D printable conductive inks for fabrication of conductive scaffold structures applicable as liquid sensors.
Carbon nanotube enabled nanocomposites have received much attention as a highly attractive alternative to conventional composite materials due to their mechanical, electrical, thermal, barrier and chemical properties such as electrical conductivity, increased tensile strength, improved heat deflection temperature, or flame retardancy. In new work, researchers report the fabrication of highly conductive carbon nanotube/polylactic acid nanocomposites used as 3D printable conductive inks for fabrication of conductive scaffold structures applicable as liquid sensors.
Oct 6th, 2016
 Researchers demonstrate a completely new micro-array design that is looking at capture and detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from an entirely new perspective. As an alternative to invasive biopsies, capturing CTCs is of great interest for evaluating cancer dissemination, predicting patient prognosis, and also for the evaluation of therapeutic treatments, representing a reliable potential alternative to invasive biopsies and subsequent proteomic and functional genetic analysis. The new approach is based on a static isolation in the form of micro-arrays of single-walled carbon nanotubes.
Researchers demonstrate a completely new micro-array design that is looking at capture and detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from an entirely new perspective. As an alternative to invasive biopsies, capturing CTCs is of great interest for evaluating cancer dissemination, predicting patient prognosis, and also for the evaluation of therapeutic treatments, representing a reliable potential alternative to invasive biopsies and subsequent proteomic and functional genetic analysis. The new approach is based on a static isolation in the form of micro-arrays of single-walled carbon nanotubes.
Oct 5th, 2016
 The intravenous iron-replacement product ferumoxytol and other iron oxide nanoparticles are being used for treating iron deficiency, as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging, and as drug carriers. In a new study, researchers have shown an intrinsic therapeutic effect of ferumoxytol on the growth of early mammary cancers and lung cancer metastases in liver and lungs. They showed that ferumoxytol can activate the immune system to attack cancer cells. This is the first description of an intrinsic therapeutic effect of iron oxide nanoparticles against cancer.
The intravenous iron-replacement product ferumoxytol and other iron oxide nanoparticles are being used for treating iron deficiency, as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging, and as drug carriers. In a new study, researchers have shown an intrinsic therapeutic effect of ferumoxytol on the growth of early mammary cancers and lung cancer metastases in liver and lungs. They showed that ferumoxytol can activate the immune system to attack cancer cells. This is the first description of an intrinsic therapeutic effect of iron oxide nanoparticles against cancer.
Oct 4th, 2016
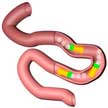 Researchers have developed an enteric micromotor consisting of a magnesium-based motor body with an enteric polymer coating. These motors, aimed controlling and enhancing site-specific delivery in the gastrointestinal tract, consist of water-powered magnesium-based tubular micromotors coated with an enteric polymer layer. The microscale robot can deliver payload to particular location via dissolution of their enteric polymeric coating to activate their propulsion at the target site towards localized tissue penetration and retention.
Researchers have developed an enteric micromotor consisting of a magnesium-based motor body with an enteric polymer coating. These motors, aimed controlling and enhancing site-specific delivery in the gastrointestinal tract, consist of water-powered magnesium-based tubular micromotors coated with an enteric polymer layer. The microscale robot can deliver payload to particular location via dissolution of their enteric polymeric coating to activate their propulsion at the target site towards localized tissue penetration and retention.
Sep 27th, 2016
 Solar cells absorb incoming sunlight and convert a part of photon energy into electricity. The remainder of photon energy is dissipated as heat. Although the idea is rather counter-intuitive, 'reverse solar cell' systems can also generate electric power by emitting rather than absorbing photons. Such systems - known as thermoradiative cells - generate voltage and electric power via non-equilibrium thermal radiation of infrared photons. Thermoradiative cells offer an opportunity to generate clean energy by harvesting radiation from largely untapped terrestrial thermal emission sources, potentially including the Earth itself.
Solar cells absorb incoming sunlight and convert a part of photon energy into electricity. The remainder of photon energy is dissipated as heat. Although the idea is rather counter-intuitive, 'reverse solar cell' systems can also generate electric power by emitting rather than absorbing photons. Such systems - known as thermoradiative cells - generate voltage and electric power via non-equilibrium thermal radiation of infrared photons. Thermoradiative cells offer an opportunity to generate clean energy by harvesting radiation from largely untapped terrestrial thermal emission sources, potentially including the Earth itself.
 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology Spotlight feed





