Microtubules, essential structural elements in living cells, grow stiffer as they grow longer, an unexpected property that could lead to advances in nano-materials development, an international team of biophysicists has found.
Jul 10th, 2006
Read more
Using a synthetic peptide modeled after the protein that the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) uses to enter cells, a multi-institutional research team has created quantum dots that can penetrate the cell membrane and image internal structures in a cell.
Jul 10th, 2006
Read more
By combining the properties of inorganic and organic molecules in one material, researchers have developed a new class of nanomaterials that can be used to create multifunctional nanoparticles
Jul 10th, 2006
Read more
Researchers have created a targeting agent that binds to a molecule found only on healthy pancreatic tissue. They then used this peptide to create a multifunctional nanoparticle-based imaging agent.
Jul 10th, 2006
Read more
Various types of carbon-based nanomaterials, such as buckyballs and nanotubes, have shown promise as drug delivery tools and imaging agents, but reports of toxicity associated with some of these materials have raised questions about their ultimate utility in clinical oncology. Three recent reports in the literature provide new insights into why certain carbon-based nanomaterials are toxic to cells and others are not.
Jul 10th, 2006
Read more
A research team at Carnegie Mellon University has discovered a nanocrystalline material that is cheaper, more stable and produces a higher quality energy storage capacity for use in a variety of industrial and portable consumer electronic products.
Jul 10th, 2006
Read more
Two physicists at the University of Copenhagen have attained unsurpassed control of the migration of electrons in a nano-transistor.
Jul 10th, 2006
Read more
New research at The University of Nottingham in the UK could help to prevent the harmful blood clots associated with heart disease and stroke.
Jul 7th, 2006
Read more
Gold nanoparticles can stabilise enzymes at air?water interfaces, enhancing their applications as biocatalysts.
Jul 7th, 2006
Read more
Researchers have created organic gel nanomaterials that could be used to encapsulate pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic products and to build 3-D biological scaffolds for tissue engineering.
Jul 7th, 2006
Read more
Implants are prone to infection, forcing patients back to surgery for repair or replacement. Now, for the first time, a team of engineers has shown that zinc or titanium oxide nanosurfaces can reduce the presence of bacteria, a technique that can be applied to implants to reduce the number of these costly and debilitating infections.
Jul 7th, 2006
Read more
 A substance used in nanotechnology contains unusual structures at its surface, a team of researchers at the Argonne National Laboratory have learned.
A substance used in nanotechnology contains unusual structures at its surface, a team of researchers at the Argonne National Laboratory have learned.
Jul 6th, 2006
Read more
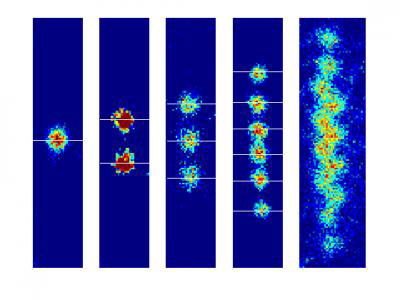 Physicists at NIST have designed and built a novel electromagnetic trap for ions that could be easily mass produced to potentially make quantum computers large enough for practical use.
Physicists at NIST have designed and built a novel electromagnetic trap for ions that could be easily mass produced to potentially make quantum computers large enough for practical use.
Jul 6th, 2006
Read more
NIST and the University of Maryland have joined in a cooperative program to develop measurement technology and other new tools designed to support all phases of nanotechnology development, from discovery to manufacture.
Jul 6th, 2006
Read more
Scientists have discovered something new about exotic particles called solitons.
Jul 6th, 2006
Read more
Researchers at Purdue University are using a rare type of electron microscope to see how structures like carbon nanotubes form at the atomic level, information that will be crucial for nanotechnology to find practical applications in computing, electronics and other areas.
Jul 5th, 2006
Read more



 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed