Watch footage of how nanotubes form
Scientists have successfully produced live video footage that shows how carbon nanotubes form.
Mar 2nd, 2007
Read more
Scientists have successfully produced live video footage that shows how carbon nanotubes form.
Mar 2nd, 2007
Read moreFifteen teams from 12 universities have been selected to present their new product ideas at the Nano Idea to Product Competition April 2-4.
Mar 2nd, 2007
Read more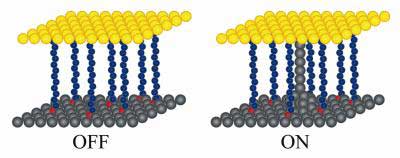 Nanoscale electrical switches can be built from self-assembled layers of organic molecules on silver wires.
Nanoscale electrical switches can be built from self-assembled layers of organic molecules on silver wires.
Mar 2nd, 2007
Read more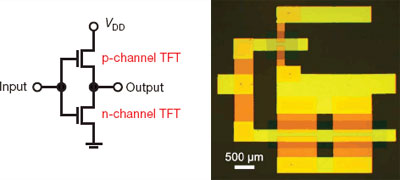 Scientists construct complementary circuits from organic materials.
Scientists construct complementary circuits from organic materials.
Mar 2nd, 2007
Read more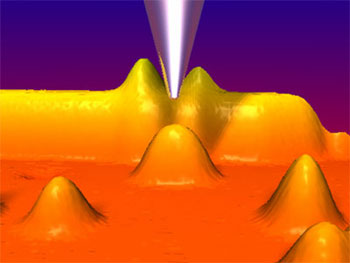 Scientists measure the magnetic interaction between single atoms.
Scientists measure the magnetic interaction between single atoms.
Mar 2nd, 2007
Read moreOne of the world's largest polymer manufacturers says that the future of material sciences is closely linked to nanotechnology.
Mar 2nd, 2007
Read moreA new computer modeling approach to study how materials behave under stress at the atomic level, offering insights that could help engineers design materials with an ideal balance between strength and resistance to failure.
Mar 1st, 2007
Read more A Slow News Friday story on Thursday...
A Slow News Friday story on Thursday...
Mar 1st, 2007
Read more New class of nanomaterials could lead to more efficient solar cells, brighter LEDs.
New class of nanomaterials could lead to more efficient solar cells, brighter LEDs.
Mar 1st, 2007
Read moreMar 1st, 2007
Read moreAward allows researcher to explore new avenue in Parkinson's therapy development.
Mar 1st, 2007
Read more A unique transmission electron microscope for the high-resolution phase contrast imaging of biologic materials.
A unique transmission electron microscope for the high-resolution phase contrast imaging of biologic materials.
Mar 1st, 2007
Read more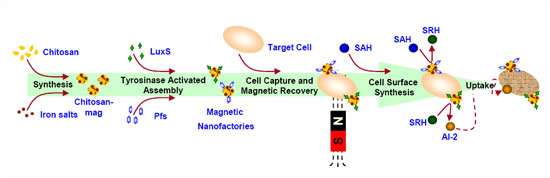 One day you may swallow tiny 'nanofactories', biochemical machines that act like cells, to deliver medicine.
One day you may swallow tiny 'nanofactories', biochemical machines that act like cells, to deliver medicine.
Mar 1st, 2007
Read moreThe U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) announced the release of a new progress report, Progress Toward Safe Nanotechnology in the Workplace.
Mar 1st, 2007
Read more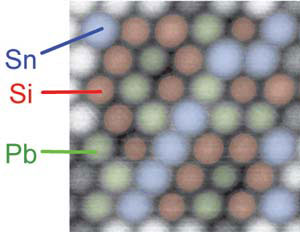 Researchers have demonstrated for the first time that atomic force microscopy can be used to reveal the chemical identity of individual atoms on a surface at room temperature.
Researchers have demonstrated for the first time that atomic force microscopy can be used to reveal the chemical identity of individual atoms on a surface at room temperature.
Mar 1st, 2007
Read more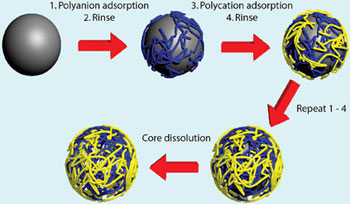 How non-covalent interactions can be used for layer-by-layer surface modification.
How non-covalent interactions can be used for layer-by-layer surface modification.
Feb 28th, 2007
Read more