 A conference focused on the development of common nanotechnology-enabled platforms that will drive innovation and spur commercial opportunities in a broad array of industries, including nanoelectronics, health care, energy, defense and aerospace, among others.
A conference focused on the development of common nanotechnology-enabled platforms that will drive innovation and spur commercial opportunities in a broad array of industries, including nanoelectronics, health care, energy, defense and aerospace, among others.
Mar 6th, 2007
Read more
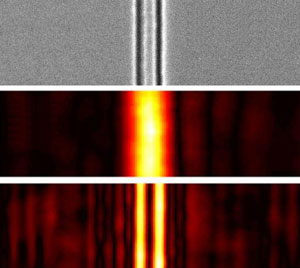 US scientists have developed a lens that can transmit images over long distances with a resolution that is not restricted by light wavelength.
US scientists have developed a lens that can transmit images over long distances with a resolution that is not restricted by light wavelength.
Mar 6th, 2007
Read more
Nokia and the University of Cambridge in the U.K. have agreed to collaborate in several areas of long-term research, beginning with nanotechnology.
Mar 6th, 2007
Read more
In experiments with laboratory mice that bear aggressive human breast cancers, researchers have used hot nanoprobes to slow the growth of tumors - without damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Mar 6th, 2007
Read more
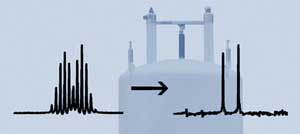 Researchers have improved a technique that simplifies the NMR spectra of mixtures, enabling the spectrum of each individual component to be seen.
Researchers have improved a technique that simplifies the NMR spectra of mixtures, enabling the spectrum of each individual component to be seen.
Mar 6th, 2007
Read more
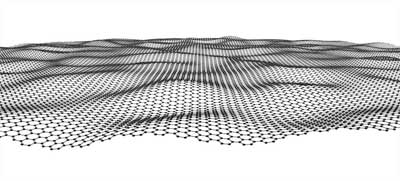 Scientists fabricate ultra-thin membranes.
Scientists fabricate ultra-thin membranes.
Mar 6th, 2007
Read more
Lockheed Martin has designed and patented a scanner based on the principle of quantum entanglement.
Mar 6th, 2007
Read more
Nanotechnology could give developing nations new ways to diagnose and treat disease and make clean water more available.
Mar 5th, 2007
Read more
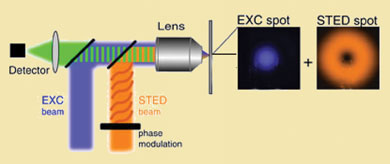 How to break the 'impenetrable barrier' of optical microscopy.
How to break the 'impenetrable barrier' of optical microscopy.
Mar 5th, 2007
Read more
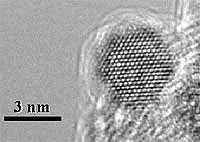 An advanced concept in nanoscale catalyst engineering - a combination of experiments and simulations that will bring polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells for hydrogen-powered vehicles closer to massive commercialization.
An advanced concept in nanoscale catalyst engineering - a combination of experiments and simulations that will bring polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells for hydrogen-powered vehicles closer to massive commercialization.
Mar 5th, 2007
Read more
Ultrafine nanoparticles made of a lacy web of polymer and tiny pockets of water may prove to be an ideal vehicle for delivering light-activated drugs to tumors.
Mar 5th, 2007
Read more
Using nanoparticles targeted to the tiny blood vessels that surround even the smallest tumors, researchers have developed a radioactive imaging agent that was able to identify human tumors.
Mar 5th, 2007
Read more
Magnetic nanocrystalline iron-nickel alloys can effectively carry and release anticancer agents.
Mar 5th, 2007
Read more
Administering a small amount of a potent but potentially toxic anticancer agent along with nanoparticles loaded with a second anticancer agent produced a dramatic inhibition of tumor growth in normally intractable cancers.
Mar 5th, 2007
Read more
Canon expects to win a patent-related dispute in the U.S.
Mar 5th, 2007
Read more
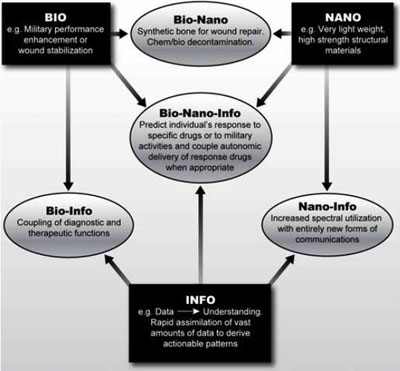 The military's quest for 'game-changing' technology.
The military's quest for 'game-changing' technology.
Mar 2nd, 2007
Read more
 A conference focused on the development of common nanotechnology-enabled platforms that will drive innovation and spur commercial opportunities in a broad array of industries, including nanoelectronics, health care, energy, defense and aerospace, among others.
A conference focused on the development of common nanotechnology-enabled platforms that will drive innovation and spur commercial opportunities in a broad array of industries, including nanoelectronics, health care, energy, defense and aerospace, among others.






 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed