Imagine a solar panel more efficient than today's best solar panels, but using 10 000 times less material. This is what EPFL researchers expect given recent findings on these tiny filaments called nanowires.
Apr 8th, 2013
Read more
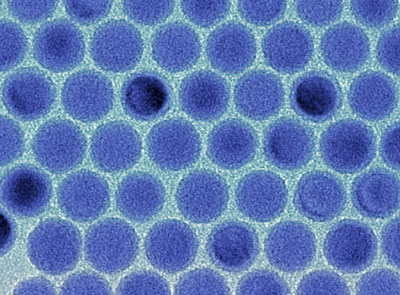 More powerful batteries could help electric cars achieve a considerably larger range and thus a breakthrough on the market. A new nanomaterial for lithium ion batteries developed in the labs of chemists at ETH Zurich and Empa could come into play here.
More powerful batteries could help electric cars achieve a considerably larger range and thus a breakthrough on the market. A new nanomaterial for lithium ion batteries developed in the labs of chemists at ETH Zurich and Empa could come into play here.
Apr 8th, 2013
Read more
Genes from the family of bacteria that produce vinegar, Kombucha tea and nata de coco have become stars in a project - which scientists today said has reached an advanced stage - that would turn algae into solar-powered factories for producing the 'wonder material' nanocellulose.
Apr 7th, 2013
Read more
 An entirely new way of thinking about pharmaceuticals - this is the goal of Morten Meldal , one of two new 'Lighthouse Professors' in chemistry at the University of Copenhagen. Meldal, 59, has been appointed by UCPH's Department of Chemistry to establish the soon to be Evolutionary Chemical Biology research centre. Along with the appointment, 35 million kroner has been granted by the University to get the centre up and running.
An entirely new way of thinking about pharmaceuticals - this is the goal of Morten Meldal , one of two new 'Lighthouse Professors' in chemistry at the University of Copenhagen. Meldal, 59, has been appointed by UCPH's Department of Chemistry to establish the soon to be Evolutionary Chemical Biology research centre. Along with the appointment, 35 million kroner has been granted by the University to get the centre up and running.
Apr 7th, 2013
Read more
 As prostate cancer progresses, the cancer cells become more resistant to traditional treatments such as chemotherapy and they become more aggressive and spread more rapidly. But now, a Temple School of Pharmacy researcher is exploring the use of nanotechnology to effectively treat latter-stage prostate cancer.
As prostate cancer progresses, the cancer cells become more resistant to traditional treatments such as chemotherapy and they become more aggressive and spread more rapidly. But now, a Temple School of Pharmacy researcher is exploring the use of nanotechnology to effectively treat latter-stage prostate cancer.
Apr 7th, 2013
Read more
Scientific research developed through an innovative fund will help find solutions to combat world hunger and poverty. Last week, the government announced Canada's contribution to the second phase of the Canadian International Food Security Research Fund (CIFSRF).
Apr 6th, 2013
Read more
 A UB-led research team recently traveled to Zimbabwe to participate in a week-long program of workshops that included the formal launch of two Zimbabwe national programs: the Zimbabwe International Nanotechnology Center (ZINC) and the Zimbabwe Evidence-To-Action (ETA), an implementation project to eradicate HIV/AIDS in Zimbabwe.
A UB-led research team recently traveled to Zimbabwe to participate in a week-long program of workshops that included the formal launch of two Zimbabwe national programs: the Zimbabwe International Nanotechnology Center (ZINC) and the Zimbabwe Evidence-To-Action (ETA), an implementation project to eradicate HIV/AIDS in Zimbabwe.
Apr 6th, 2013
Read more
 Rice University physicists on the hunt for the origins of high-temperature superconductivity have published new findings this week about a seemingly contradictory state in which a material simultaneously exhibits the conflicting characteristics of both a metallic conductor and an insulator.
Rice University physicists on the hunt for the origins of high-temperature superconductivity have published new findings this week about a seemingly contradictory state in which a material simultaneously exhibits the conflicting characteristics of both a metallic conductor and an insulator.
Apr 5th, 2013
Read more
A research team has made a fundamental breakthrough in single-crystal X-ray analysis, the most powerful method for molecular structure determination.
Apr 5th, 2013
Read more
Scientists developed the technology to produce gold nanoparticles biologically.
Apr 5th, 2013
Read more
Four CNSE student teams are among the semifinal winners moving to the final round after presentations highlighting their world-class education and access to the college's unparalleled resources.
Apr 5th, 2013
Read more
Bruker is hosting webinar for AFM and 3D optical microscope users.
Apr 5th, 2013
Read more
When light hits organic molecules, it triggers processes that are of considerable interest to scientists. But the individual steps of the reaction are very hard to identify. A study group at the University of W�rzburg has now accomplished this task - with a sophisticated approach.
Apr 5th, 2013
Read more
 Researchers could show that exhaled human breath contains a characteristic molecular 'fingerprint'. The scientists want to use this finding to diagnose diseases based on the chemical analysis of patient's exhaled breath, using highly sensitive and precise instrumental methods.
Researchers could show that exhaled human breath contains a characteristic molecular 'fingerprint'. The scientists want to use this finding to diagnose diseases based on the chemical analysis of patient's exhaled breath, using highly sensitive and precise instrumental methods.
Apr 4th, 2013
Read more
Talk about storing data in the cloud. Scientists at the Joint Quantum Institute (JQI) of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Maryland have taken this to a whole new level by demonstrating that they can store visual images within quite an ethereal memory device - a thin vapor of rubidium atoms. The effort may prove helpful in creating memory for quantum computers.
Apr 4th, 2013
Read more
Funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), the research focuses on membranes that could provide solutions to worldwide problems; from stopping power stations releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, to detecting the chemical signals produced by agricultural pests.
Apr 4th, 2013
Read more







 Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Nanotechnology News feed