China to build 'brain database'
Chinese scientists are planning to build a 'brain database' in a bid to identify clues to tackling cerebral diseases and related disorders.
Jun 30th, 2014
Read more
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Chinese scientists are planning to build a 'brain database' in a bid to identify clues to tackling cerebral diseases and related disorders.
Jun 30th, 2014
Read more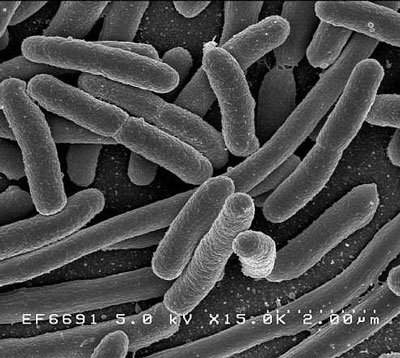 Researchers have demonstrated that when exposed to repeated cycles of antibiotics, within days bacteria can evolve a new adaptation, by remaining dormant for the treatment period to survive antibiotic stress. The results show for the first time that bacteria can develop a biological timer to survive antibiotic exposure. With this new understanding, scientists could develop new approaches for slowing the evolution of antibiotic resistance.
Researchers have demonstrated that when exposed to repeated cycles of antibiotics, within days bacteria can evolve a new adaptation, by remaining dormant for the treatment period to survive antibiotic stress. The results show for the first time that bacteria can develop a biological timer to survive antibiotic exposure. With this new understanding, scientists could develop new approaches for slowing the evolution of antibiotic resistance.
Jun 30th, 2014
Read more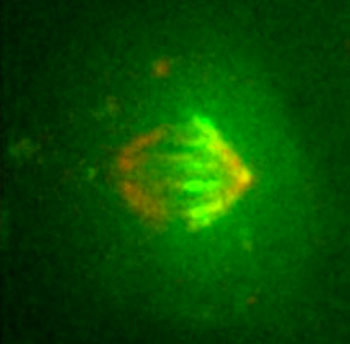 By labelling the ends of thousands of microtubules, which are indispensable and extremely dynamic and variable, researchers have finally been able to follow their distribution and movement during the assembly of the mitotic spindle.
By labelling the ends of thousands of microtubules, which are indispensable and extremely dynamic and variable, researchers have finally been able to follow their distribution and movement during the assembly of the mitotic spindle.
Jun 30th, 2014
Read moreWith the plethora of research and published studies on stem cells over the last decade, many would say that the definition of stem cells is well established and commonly agreed upon. However, a new review article suggests that scientists have only scratched the surface of understanding the nature, physiology and location of these cells.
Jun 30th, 2014
Read moreResearchers have made a giant leap towards the goal of 'bio-printing' transplantable tissues and organs for people affected by major diseases and trauma injuries, a new study reports.
Jun 30th, 2014
Read more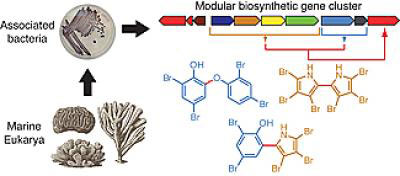 Scientists have discovered a widely distributed group of marine bacteria that produce compounds nearly identical to toxic man-made fire retardants.
Scientists have discovered a widely distributed group of marine bacteria that produce compounds nearly identical to toxic man-made fire retardants.
Jun 29th, 2014
Read moreResearchers have developed new methods to trace the life history of individual cells back to their origins in the fertilised egg. By looking at the copy of the human genome present in healthy cells, they were able to build a picture of each cell's development from the early embryo on its journey to become part of an adult organ.
Jun 29th, 2014
Read moreNew light-sensitive protein enables simpler, more powerful optogenetics.
Jun 29th, 2014
Read moreStudy presents a new theoretical foundation explaining the mechanism of protein folding and unfolding in water.
Jun 26th, 2014
Read more Scientists have found a 'Trojan horse' way to deliver proteins into live human cells without damaging them. The finding is expected to be easily adopted for use in medical research to find cures and treatments for a wide range of diseases.
Scientists have found a 'Trojan horse' way to deliver proteins into live human cells without damaging them. The finding is expected to be easily adopted for use in medical research to find cures and treatments for a wide range of diseases.
Jun 26th, 2014
Read more Scientists are reporting the next step in the evolution of wound treatment with a material that leads to faster healing than existing commercial dressings and prevents potentially harmful bacteria from sticking.
Scientists are reporting the next step in the evolution of wound treatment with a material that leads to faster healing than existing commercial dressings and prevents potentially harmful bacteria from sticking.
Jun 25th, 2014
Read more Scientists report a clearer understanding of how mussels stick to surfaces, which could lead to new classes of adhesives that will work underwater and even inside the body.
Scientists report a clearer understanding of how mussels stick to surfaces, which could lead to new classes of adhesives that will work underwater and even inside the body.
Jun 25th, 2014
Read more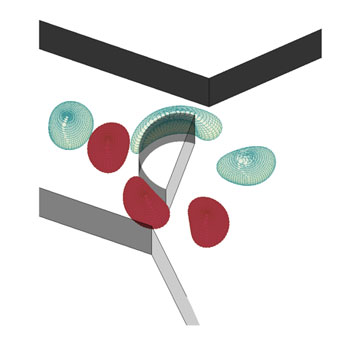 A device proposed by researchers at Sweden's KTH Royal Institute of Technology could offer a more reliable alternative for detecting biomarkers in patients facing such illnesses as cancer or malaria.
A device proposed by researchers at Sweden's KTH Royal Institute of Technology could offer a more reliable alternative for detecting biomarkers in patients facing such illnesses as cancer or malaria.
Jun 25th, 2014
Read more This review article summarizes the structure and stability of all the minichromosomes that Minoru Murata and colleagues at Okayama University have isolated since 2006, and describes their interesting features.
This review article summarizes the structure and stability of all the minichromosomes that Minoru Murata and colleagues at Okayama University have isolated since 2006, and describes their interesting features.
Jun 25th, 2014
Read more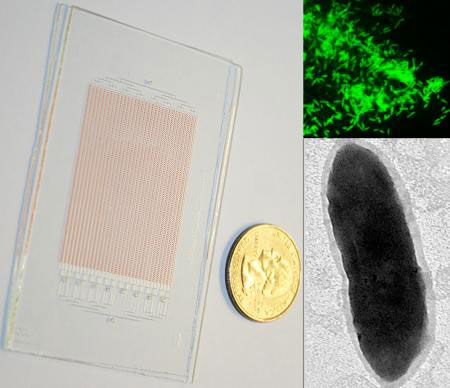 Trillions of bacteria live in the human body, and although there's plenty of evidence that these microbes play a collective role in human health, we know very little about the individual bacterial species. Employing the use of a specially designed glass chip with tiny compartments, researchers provide a way to target and grow specific microbes from the gut - a key step in understanding which bacteria are helpful to human health and which are harmful.
Trillions of bacteria live in the human body, and although there's plenty of evidence that these microbes play a collective role in human health, we know very little about the individual bacterial species. Employing the use of a specially designed glass chip with tiny compartments, researchers provide a way to target and grow specific microbes from the gut - a key step in understanding which bacteria are helpful to human health and which are harmful.
Jun 24th, 2014
Read more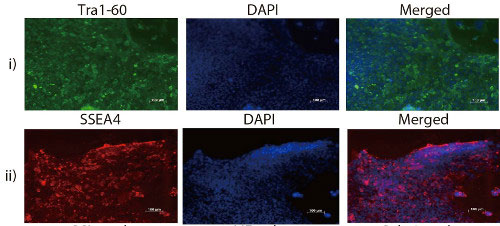 Researchers gained new insight into the role of CCL2, a chemokine known to be involved in the immune response, in the enhancement of stem cell pluripotency. In the study, the researchers replaced basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), a critical component of human stem cell culture, with CCL2 and studied its effect.
Researchers gained new insight into the role of CCL2, a chemokine known to be involved in the immune response, in the enhancement of stem cell pluripotency. In the study, the researchers replaced basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), a critical component of human stem cell culture, with CCL2 and studied its effect.
Jun 24th, 2014
Read more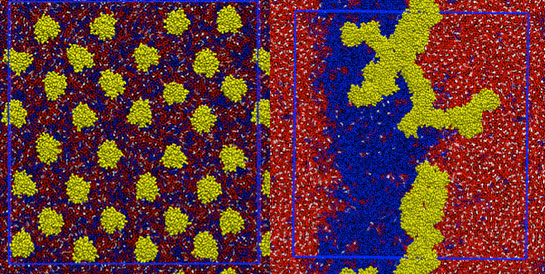 Supercomputer simulations reveal clusters of a protein linked to cancer warp cell membranes - findings could help design new anticancer drugs.
Supercomputer simulations reveal clusters of a protein linked to cancer warp cell membranes - findings could help design new anticancer drugs.
Jun 23rd, 2014
Read moreVarious genes of the plant Arabidopsis thaliana and of the bacteria Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas fluorescens could be used as early biomarkers of stress due to heavy metals.
Jun 23rd, 2014
Read more