Cryptocurrencies
Content
– What is Cryptocurrency?
– What is the Purpose of Cryptocurrencies?
– Mined vs Non-mined Cryptocurrency
– What is Staking Coins?
– How Much Can You Earn with Staking?
– Are Cryptocurrencies Legal?
– How Secure are Cryptocurrencies?
– How to Buy and Sell Cryptocurrency
– Cryptocurrency Wallets
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a form of digital currency that has an open and decentralized system and uses cryptography to enhance security and control the creation of new currency units.
The units of a cryptocurrency are called coins or tokens and exist on a distributed and decentralized ledger called a blockchain.
The first cryptocurrency was Bitcoin, introduced in 2010, which continues to lead the pack of cryptocurrencies in terms of market capitalization, user base, and popularity.
There are thousand of cryptocurrencies (almost 8000 in November 2021). You can find a comprehensive list here including market data such as price, volume and market capitalization.

What is the Purpose of Cryptocurrencies?
Good question – if and what purpose cryptocurrencies have is a highly controversial discussion. Proponents are adamant that the coins are money. However, when objectively looking at crypto tokens a few characteristics stand out.
You still can’t use bitcoin or other crypto tokens as a medium for daily transactions. However, it has become very popular for criminal activities for instance ransomware demands payable in bitcoin.
Apart from buying and selling NFTs, most purchases of physical items conducted with bitcoin tokens take the form of countertrade. That means that the token, priced in fiat currency like dollar or euro, is compared to a good or service, priced in fiat currency, and from this comparison of two fiat currency prices emerges an exchange ratio between the token and the good or service.
For example, if a newspaper subscription costs $20 per month and the publisher allows you to buy with bitcoin, the $20 would be converted into bitcoin at the time of your order. The transaction goes through an intermediary and the publisher will receive $20 (minus a commission). If you were to sign up for a subscription one day later, the dollar price still would be $20 but you would pay more or less, depending on the bitcoin value – which fluctuates widely.
This brings us to the main reason people are using cryptocurrency: speculation. People buy a crypto tokens with fiat currency with an intention to later sell it for fiat currency and make a profit. This speculation drives volatility in the fiat currency price of tokens.
This volatility, combined with the fact that you can’t use cryptos for purchasing everyday goods and services, makes clear that cryptocurrencies don’t have the characteristics that we commonly associate with ‘money’.
Mined vs Non-mined Cryptocurrency
The term mining is used as a metaphor for creating new coins of a currency, since it requires (computational) work just as mining natural resources requires (physical) work. The tokens that miners find are virtual and exist only within the digital ledger of the cryptocurrency’s blockchain. Read all about mining in our primer on Bitcoin mining.
Mining bitcoins, or any other cryptocurrency for that matter, verifies transactions by evaluating them against the transactions that happened before. This is an essential function of cryptocurrency as it prevents double-spending, collects transaction fees and creates the coin supply.
Participants – known as miners – compete to earn bitcoins by applying computing power in a process known as Proof-of-Work (PoW) to add new blocks to the chain that constitutes the ledger (the blockchain). The process is named PoW because only miners who have proven to have dedicated sufficient resources (work) will have a chance at mining bitcoins.
Non-mined virtual currencies operate on a model known as Proof-of-Stake (PoS). They don’t require massive computing power (and the associated high energy consumption, which means the costs for this method are substantially lower) and competition among miners to validate a block of transactions. Instead, In its original version Proof-of-Stake hinges on the idea that, for a user, the likelihood to confirm the next block is positively related to the amount of currency units held in the wallet, and possibly also on the time length which the money has been unspent for.
In essence, this means that the more of a cryptocurrency someone owns, and the longer they have held that cryptocurrency for, the more likely they are to be chosen to validate a block of transactions.
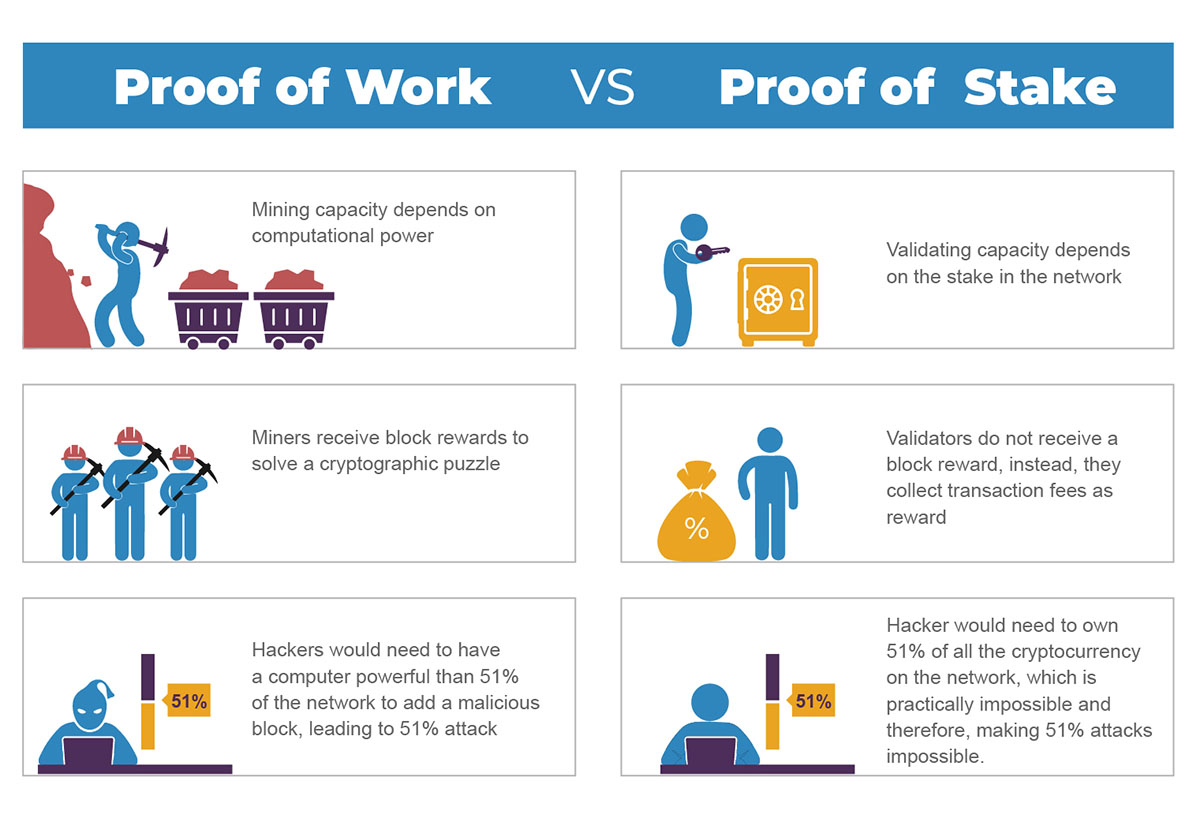
The biggest difference between Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake is their energy usage. For PoW, large mining farms around the world are competing with each other and are computing the same problems – in the process using massive amounts of energy. In contrast, PoS doesn't require validators to all solve complex equations and therefore is a much eco-friendlier way to verify transactions.
Also, Proof-of-Stake are different from rewards for Proof-of-Work miners. Instead of being paid in newly mined tokens or fractions of a token, stakeholders receive the aggregate transaction fees from a block of transactions.
For PoS crypto networks, when a block of transactions is ready to be processed and added to the chain, the cryptocurrency's proof-of-stake protocol will choose a validator node to review the block. The validator checks if the transactions in the block are accurate. If so, they add the block to the blockchain and receive a reward (the aggregate transaction fees ) for their contribution. As a safeguard, if a validator proposes adding a block with inaccurate information, they lose some of their staked holdings as a penalty.
In theory, anyone staking crypto could be chosen as a validator, but the odds are very low if you are staking only a small amount. For this reason, most token owners join large staking pools such as crypto exchanges.
What is Staking Coins?
Major Proof-of-Stake coins, all with their own blockchains, are Ethereum, Solana, Cardano, Tezos, Polkadot and Celo. You can find a comprehensive list here including market data such as price, volume and market capitalization.
Staking coins is when you pledge your coins to be used for PoS verification transactions. Your coins are locked up while you stake them, but you can un-stake them at any time if you want to trade them.
You can begin staking cryptocurrency independently if you own the required minimum amount for staking. This amount varies substantially from coin to coin. For instance, the minimum fixed ADA staking fee across the Cardano (ADA) network is 340 ADA (worth about $600 at the time of writing). In the case of Ethereum 2.0 (ETH), staking requires a minimum deposit of 32 ETH (worth about $144,000 at the time of writing).
If the number of coins you hold is smaller than the required minimum for staking your only other option is to join a staking pool. For instance, if you are holding your coins in an exchange-hosted crypto wallet, the exchange handles all the staking on the backend, and you simply have to hold the crypto in your wallet.
How Much Can You Earn with Staking?
Staking is passive income, a bit like receiving dividends on stocks you own. The amount you earn varies from crypto to crypto.
If you want to stake coins, you need to own a cryptocurrency that uses the proof-of-stake model – it doesn’t work with cryptocurrencies using the Point-of-Work model, like bitcoin. Then you can choose the amount you want to stake. You can do this through many popular cryptocurrency exchanges.
If you join a staking pool your rewards will be a percentage of the rewards earned by the pool equivalent to your coin’s share in the pool.
Here is a nifty calculator that lets you calculate your earnings from staking a specific coin.
Are Cryptocurrencies Legal?
That depends country by country. Cryptocurrencies are legal in the U.S. and broadly considered legal across the European Union, but cryptocurrency exchange regulations depend on individual member states. China, however, has essentially banned their use. Other countries that have banned them or restrict their use at the time of this writing include Algeria, India, Iran, Irak, Nepal, Colombia, Turkey, Indonesia, Bolivia, Russia, Vietnam and Egypt.
How Secure are Cryptocurrencies?
Most cryptocurrencies are built using blockchain technology, which is hard for hackers to tamper with. In addition, transactions require a two-factor authentication process.
So, while securities are in place, that doesn't mean cryptocurrencies are un-hackable. In fact, several high-dollar hacks have cost cryptocurrency startups heavily. This is especially true for exchange platforms that allow people to buy and sell digital coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum, and a place where many people leave their coins for safekeeping.
However, the safety of exchanges is questionable. Dozens of hacks against cryptocurrency platforms have seen at least $2bn stolen by hackers since 2014.
The largest-ever cryptocurrency hacks (so far...):
BitGrail: $146m was hacked from the Italian exchange in 2018. It's estimated that 230,000 BitGrail users lost funds.
KuCoin: $281m was stolen by suspected North Korean hackers from this attack on the Seychelles-based exchange in 2020. The company recovered most of the funds and refunded customers.
MtGox: $450m of mainly Bitcoin was hacked in 2014 which collapsed the Japanese exchange. None of the customers have been reimbursed yet.
Coincheck: $534m was stolen in 2018 from the Japanese exchange. Customers were eventually reimbursed.
Poly Network: $610m was hacked from the Chinese platform earlier this month in various coins. The hacker returned all the funds and customers have started being reimbursed.
Add to this frequent spam attempts and fraudulent coin schemes and it becomes clear that today’s cryptocurrency environment is not for the fainthearted.
How to Buy and Sell Cryptocurrency
Some cryptocurrencies are available for purchase with fiat currency like euros or U.S. dollars, while others require that you pay with bitcoins or another cryptocurrency.
Generally, you create an account on a cryptocurrency exchange or with a growing number of online brokers that offer cryptocurrencies, and then you can transfer real money to buy cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin or Ethereum.
There are now hundreds of these Cryptocurrency Spot Exchanges (here is a list) and keeping an overview and understand the differences can be confusing. So, before you invest one dollar, inform yourself and learn about cryptocurrency exchanges – do your research, read reviews and talk with more experienced investors.
Cryptocurrency Wallets
To store cryptocurrencies yourself, you’ll need a cryptocurrency wallet, an online app that can hold your currency. In simple terms, a cryptowallet is a program that stores your private and public cryptographic keys, which you need to access the blockchain on your behalf and make transactions with your cryptocurrency.
Please note: Owning some cryptocurrency and storing it in your cryptowallet doesn’t mean you got the coins in your pocket. The wallet is just two keys, and the coins are all in the blockchain – which they never leave. When a transaction occurs, the only thing that actually happens is a block describing the transaction is added to the blockchain.
There are different types of wallets to consider and here is a good primer to acquaint yourself with them.
Check out our SmartWorlder section to read more about smart technologies.



