| Sep 11, 2024 |
Thermosensitive hydrogel offers fast detection of nitrite
(Nanowerk News) Nitrite is commonly used as a food additive, but when ingested, it can harm the body's oxygen transport system. The World Health Organization limits nitrite to 1.0 mg/L in drinking water and 30 mg/kg in meat products. However, current nitrite detection methods are often complicated.
|
|
Recently, a team of researchers led by Prof. JIANG Changlong from Institute of Solid State Physics, the Hefei Institutes of Physical Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed a novel thermosensitive hydrogel-based fluorescence probe for real-time visualization and detection of nitrite.
|
|
They published the progress in Journal of Hazardous Materials ("Multi-deformable interpenetrating network thermosensitive hydrogel fluorescent device for real-time and visual detection of nitrite").
|
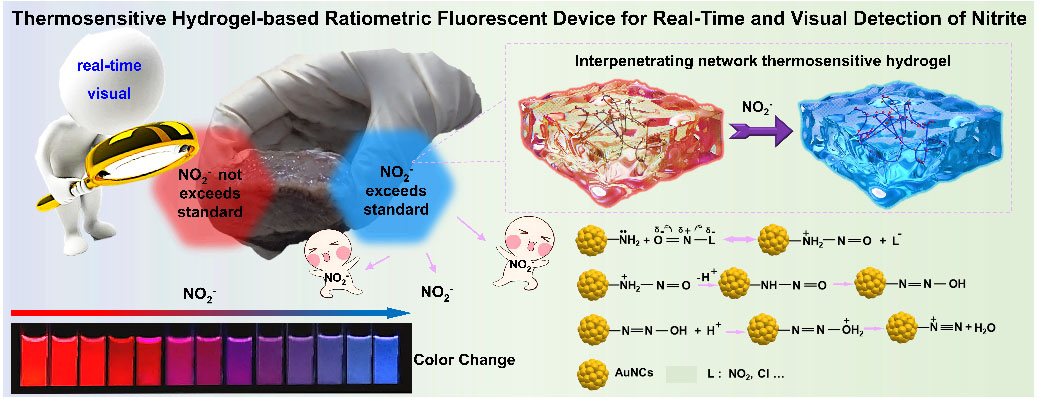 |
| Schematic representation of Au-NCs/LCG-P407 fluorescent hydrogel for the detection of nitrite. (Image: LI Lingfei) (click on image to enlarge)
|
|
"With this probe and a smartphone, the nitrite data is available at a glance,” said Dr. LI Lingfei, a member of the team.
|
|
In this research, the functionalized thermosensitive hydrogel doped with fluorescent probes was designed to make it easier to get information of nitrite. Gold nanoclusters (Au NCs) and carbon-based dots were added into the hydrogel’s multi-layered structure, which was made from P407, lignin, and cellulose. This created a material with special fluorescence properties and strong stability. The interconnected P407, lignin, and cellulose gave the hydrogel an excellent porous structure.
|
|
This novel Au NCs/LCG-P407 fluorescent hydrogel has been designed with the objective of optimizing portable and efficient device strategies. It provides a basis for further development of sensing platforms for the detection of environmental and hazardous substances in food safety.
|
|
The hydrogel sensor can also be paired with a smartphone app to visually measure NO₂⁻ in water, making detection easier and more practical.
|
|
This research marks advancement in hydrogel applications and highlights its potential to enhance food safety monitoring systems, according to the team.
|

