| Jul 26, 2024 |
New laser technique could enable data storage on printable magnetic devices
(Nanowerk News) The proliferation of all things digital doesn’t mean that printing technology is no longer relevant. In fact, printing technology is required to make the semiconductors necessary for the digital world. And as an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has shown using a new printing technique, printable magnetic devices for high-density data storage might soon be realized.
|
|
Dr. Ken-ichi Yuyama, a lecturer at the Graduate School of Science, and his colleagues report in APL Materials ("Using optical vortex laser induced forward transfer to fabricate a twisted ferrite microcrystal array") on the development of a new type of laser-induced forward transfer (LIFT) for laser printing using an optical vortex, which has been dubbed OV-LIFT.
|
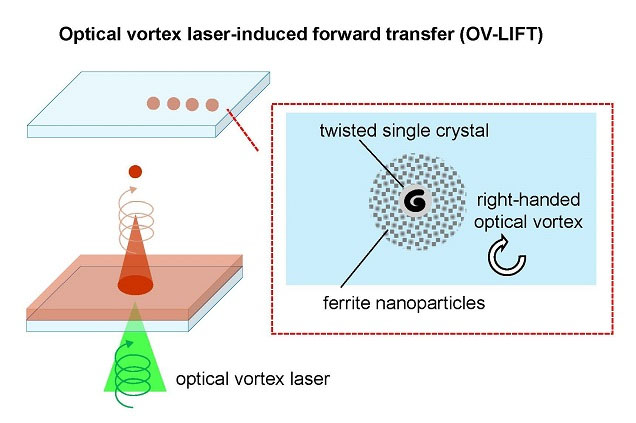 |
| A laser beam converted to an optical vortex can perform laser-induced forward transfer (LIFT) of ferrite nanoparticles resulting in twisted single crystals corresponding to the rotation of the vortex. (Image: Osaka Metropolitan University)
|
|
The team shined a laser beam on a spatial light modulator and through a quarter-wave plate to convert the beam into a circularly polarized optical vortex. This beam was then focused onto a plate with magnetic ferrite nanoparticles that were shown to successfully be printed on a surface at high precision.
|
|
The resulting printed crystals also have helix-like twisted structures, the direction of which could be controlled by changing the optical vortex’s helicity to the opposite rotation.
|
|
“The results of this research have the potential to be used not only for fine particle patterning but also for single crystal synthesis, which can be expected to lead to the development of new materials,” declared Dr. Yuyama. “We plan to apply this technology to various types of fine particles, as well as to shine a light on the formation mechanism and function of twisted crystals.”
|

