Study offers new way to discover HIV vaccine targets
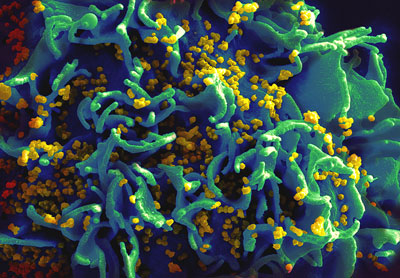 Researchers develop a method to identify weak points in viral proteins that could be exploited for vaccine development.
Researchers develop a method to identify weak points in viral proteins that could be exploited for vaccine development.
Mar 22nd, 2013
Read more
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
 Researchers develop a method to identify weak points in viral proteins that could be exploited for vaccine development.
Researchers develop a method to identify weak points in viral proteins that could be exploited for vaccine development.
Mar 22nd, 2013
Read moreNational survey finds three out of four adults have heard little or nothing about the emerging technology.
Mar 20th, 2013
Read more The road signs that direct traffic on the highways - collectively known as the cytoskeleton - are a mystery, and now the subject of research for Lee Ligon, associate professor of biology at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
The road signs that direct traffic on the highways - collectively known as the cytoskeleton - are a mystery, and now the subject of research for Lee Ligon, associate professor of biology at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
Mar 19th, 2013
Read more Illinois chemists have used DNA to do a protein's job, creating opportunities for DNA to find work in more areas of biology, chemistry and medicine than ever before.
Illinois chemists have used DNA to do a protein's job, creating opportunities for DNA to find work in more areas of biology, chemistry and medicine than ever before.
Mar 19th, 2013
Read moreScientists have accurately calculated the sliding mechanism for deciphering the second genetic code written within the DNA base pair sequence.
Mar 19th, 2013
Read moreNew research describes an advance in efforts to develop a method to replace missing teeth with new bioengineered teeth generated from a person's own gum cells.
Mar 18th, 2013
Read more For the first time, scientists have transplanted neural cells derived from a monkey's skin into its brain and watched the cells develop into several types of mature brain cells, according to the authors of a new study in Cell Reports. After six months, the cells looked entirely normal, and were only detectable because they initially were tagged with a fluorescent protein.
For the first time, scientists have transplanted neural cells derived from a monkey's skin into its brain and watched the cells develop into several types of mature brain cells, according to the authors of a new study in Cell Reports. After six months, the cells looked entirely normal, and were only detectable because they initially were tagged with a fluorescent protein.
Mar 17th, 2013
Read moreThe researchers will be able to work closely together on projects in the field of regenerative medicine, an area with a promising future. The aim is to use the strategy of marine animals to develop novel bio-inspired bone replacement materials and medications to ameliorate osteoporosis.
Mar 14th, 2013
Read more An unprecedented collaboration among academia, industry, government and civil society has resulted in the launch of a professional-grade collection of public domain DNA parts that greatly increases the reliability and precision by which biology can be engineered.
An unprecedented collaboration among academia, industry, government and civil society has resulted in the launch of a professional-grade collection of public domain DNA parts that greatly increases the reliability and precision by which biology can be engineered.
Mar 14th, 2013
Read more Predictability is often used synonymously with "boring", as in that story or that outcome was soooo predictable. For practioners of synthetic biology seeking to engineer valuable new microbes, however, predictability is the brass ring that must be captured. Researchers with the multi-institutional partnership known as BIOFAB have become the first to grab at least a portion of this ring by unveiling a package of public domain DNA sequences and statistical models that greatly increase the reliability and precision by which biological systems can be engineered.
Predictability is often used synonymously with "boring", as in that story or that outcome was soooo predictable. For practioners of synthetic biology seeking to engineer valuable new microbes, however, predictability is the brass ring that must be captured. Researchers with the multi-institutional partnership known as BIOFAB have become the first to grab at least a portion of this ring by unveiling a package of public domain DNA sequences and statistical models that greatly increase the reliability and precision by which biological systems can be engineered.
Mar 13th, 2013
Read more AMSilk, a spin-off of the Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM), has produced the world's first artificial silk fiber that is entirely made of recombinant spider silk proteins. The fiber's tensile strength is comparable to that of natural spider silk, which led to the name Biosteel.
AMSilk, a spin-off of the Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM), has produced the world's first artificial silk fiber that is entirely made of recombinant spider silk proteins. The fiber's tensile strength is comparable to that of natural spider silk, which led to the name Biosteel.
Mar 13th, 2013
Read more A simple fermentation treatment can convert a by-product of biofuel production into a valuable chemical feedstock for a wide range of biomedical products
A simple fermentation treatment can convert a by-product of biofuel production into a valuable chemical feedstock for a wide range of biomedical products
Mar 13th, 2013
Read more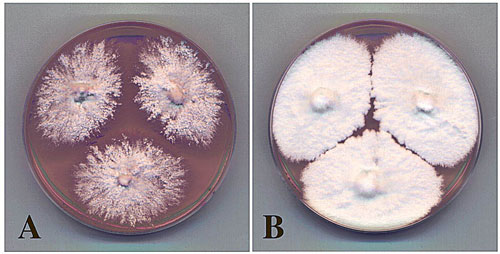 Fungi, with the exception of shitake and certain other mushrooms, tend to be something we associate with moldy bread or dank-smelling mildew. But they really deserve more respect. Fungi have fantastic capabilities and can be grown, under certain circumstances, in almost any shape and be totally biodegradable. And, if this weren't enough, they might have the potential to replace plastics one day. The secret is in the mycelia.
Fungi, with the exception of shitake and certain other mushrooms, tend to be something we associate with moldy bread or dank-smelling mildew. But they really deserve more respect. Fungi have fantastic capabilities and can be grown, under certain circumstances, in almost any shape and be totally biodegradable. And, if this weren't enough, they might have the potential to replace plastics one day. The secret is in the mycelia.
Mar 12th, 2013
Read moreThe grant will fund a collaborative project that will seek to use synthetic biology - the design and construction of biological devices and systems - to more effectively create proteins, such as those used in drug manufacture.
Mar 11th, 2013
Read moreProtein activity is strictly regulated. Incorrect or poor protein regulation can lead to uncontrolled growth and thus cancer or chronic inflammation. Researchers have identified enzymes that can regulate the activity of medically important proteins. Their discovery enables these proteins to be manipulated very selectively, opening up new treatment methods for inflammations and cancer.
Mar 11th, 2013
Read moreGroup sees such initiatives bringing new life to U.S. manufacturing.
Mar 7th, 2013
Read more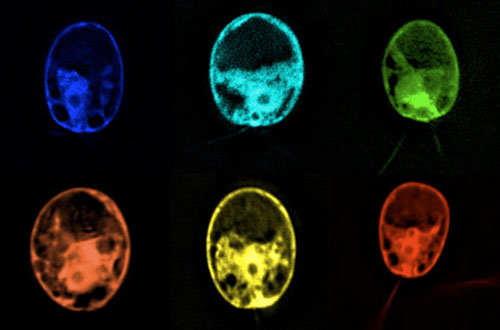 What can green algae do for science if they weren't, well, green? That's the question biologists at UC San Diego sought to answer when they engineered a green alga used commonly in laboratories, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, into a rainbow of different colors by producing six different colored fluorescent proteins in the algae cells.
What can green algae do for science if they weren't, well, green? That's the question biologists at UC San Diego sought to answer when they engineered a green alga used commonly in laboratories, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, into a rainbow of different colors by producing six different colored fluorescent proteins in the algae cells.
Mar 7th, 2013
Read moreAssistant professor receives $360,000 grant for research with potential applications in biofuel cells, pharmaceuticals and commodity chemicals.
Mar 7th, 2013
Read more