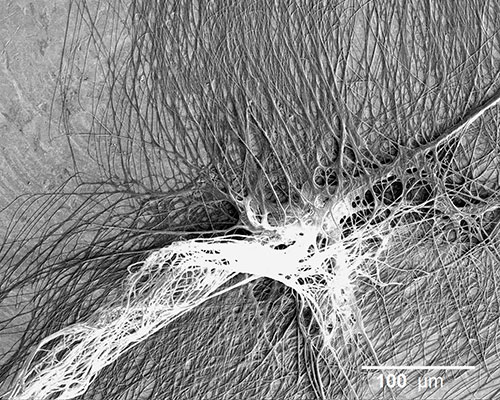
 Researchers at The University of Akron are again spinning inspiration from spider silk - this time to create more efficient and stronger commercial and biomedical adhesives that could, for example, potentially attach tendons to bones or bind fractures.
Researchers at The University of Akron are again spinning inspiration from spider silk - this time to create more efficient and stronger commercial and biomedical adhesives that could, for example, potentially attach tendons to bones or bind fractures.
May 16th, 2014
Read more
 Molecular 'fingerprint' for tissue taken from first isotope-enriched mouse has huge potential for scientific breakthroughs, as well as improved medical implants. Earliest research based on data has already revealed that a molecule thought to exist for repairing DNA may also in fact trigger bone formation.
Molecular 'fingerprint' for tissue taken from first isotope-enriched mouse has huge potential for scientific breakthroughs, as well as improved medical implants. Earliest research based on data has already revealed that a molecule thought to exist for repairing DNA may also in fact trigger bone formation.
May 16th, 2014
Read more
Participating in the program are universities from Australia, the Netherlands, and Germany.
May 16th, 2014
Read more
Innovative IBN peptide technology licensed by 3-D Matrix for medical application.
May 16th, 2014
Read more
A new set of focus groups convened by the Synthetic Biology Project at the Wilson Center found continued low awareness of synthetic biology, as well as concerns about specific applications.
May 15th, 2014
Read more
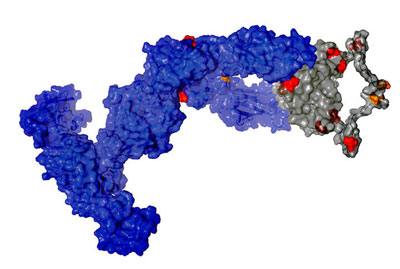 Comparing the antibodies of sharks, which are very old from an evolutionary perspective, with those of humans, a team of researchers discovered stabilizing mechanisms that can also be applied to optimize custom-tailored antibodies in humans.
Comparing the antibodies of sharks, which are very old from an evolutionary perspective, with those of humans, a team of researchers discovered stabilizing mechanisms that can also be applied to optimize custom-tailored antibodies in humans.
May 15th, 2014
Read more
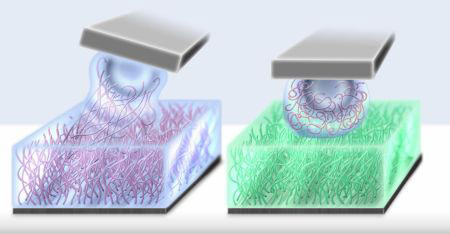 The mechanical properties of natural joints are considered unrivalled. Cartilage is coated with a special polymer layer allowing joints to move virtually friction-free, even under high pressure. Scientists have developed a new process that technologically imitates biological lubrication and even improves it using two different types of polymers.
The mechanical properties of natural joints are considered unrivalled. Cartilage is coated with a special polymer layer allowing joints to move virtually friction-free, even under high pressure. Scientists have developed a new process that technologically imitates biological lubrication and even improves it using two different types of polymers.
May 14th, 2014
Read more
The final step in the production of a biotech medicine is finishing with the correct sugar structure. This step is essential for the efficacy of the medicine, but it also makes the production process very complex and expensive. Now, researchers have developed a technology that shortens the sugar structures whilst retaining the therapeutic efficiency. This technology has the potential to make the production of biotech medicines significantly simpler and cheaper.
May 14th, 2014
Read more
 Assembling a compartment inside chloroplasts of flowering plants has the potential to improve the efficiency of photosynthesis.
Assembling a compartment inside chloroplasts of flowering plants has the potential to improve the efficiency of photosynthesis.
May 14th, 2014
Read more
Researchers have completed a 3-D map of an enzyme called Proline utilization A (PutA). PutA facilitates metabolism by adding oxygen to molecules. Mapping this enzyme will give researchers a better understanding of its function, which could help drug manufacturers create more effective drugs.
May 13th, 2014
Read more
 Chemists have figured out how to control multiple bacterial behaviors - potentially good news for the treatment of infectious diseases and other bacteria-associated issues, without causing drug resistance.
Chemists have figured out how to control multiple bacterial behaviors - potentially good news for the treatment of infectious diseases and other bacteria-associated issues, without causing drug resistance.
May 13th, 2014
Read more
New drug candidate disrupts key interaction of two proteins by mimicking one to trick the other.
May 13th, 2014
Read more
Researchers use new techniques to document how cells can conceal growth, then suddenly swell like raisins into grapes; study is a 'paradigm shift' in understanding osmotic shock that may lead to new strategies for fighting bacterial disease
May 13th, 2014
Read more
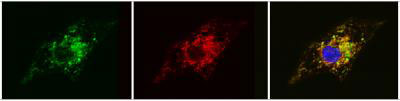 Scientists have merged stem cell and 'organ-on-a-chip' technologies to grow, for the first time, functioning human heart tissue carrying an inherited cardiovascular disease. The research appears to be a big step forward for personalized medicine, as it is working proof that a chunk of tissue containing a patient's specific genetic disorder can be replicated in the laboratory.
Scientists have merged stem cell and 'organ-on-a-chip' technologies to grow, for the first time, functioning human heart tissue carrying an inherited cardiovascular disease. The research appears to be a big step forward for personalized medicine, as it is working proof that a chunk of tissue containing a patient's specific genetic disorder can be replicated in the laboratory.
May 11th, 2014
Read more
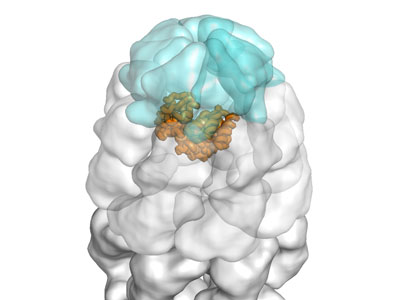 Researchers elucidate important mechanism of protein folding.
Researchers elucidate important mechanism of protein folding.
May 9th, 2014
Read more
A chemical-based DNA cleavage technique could lead to more versatile genetic engineering.
May 9th, 2014
Read more
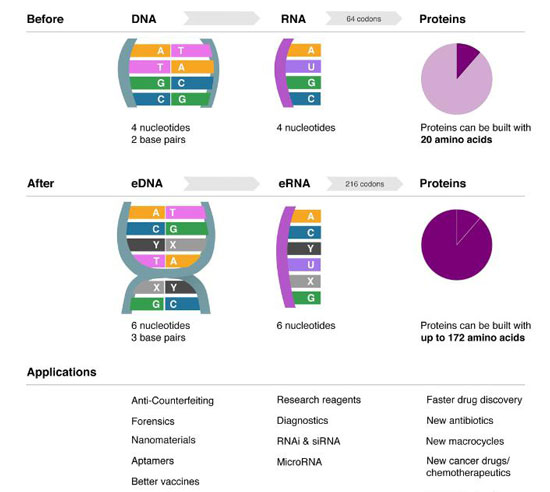 Synthorx Inc. announced the official launch of the company, which will be focused on using synthetic biology to improve the discovery and development of new medicines, diagnostics and vaccines.
Synthorx Inc. announced the official launch of the company, which will be focused on using synthetic biology to improve the discovery and development of new medicines, diagnostics and vaccines.
May 8th, 2014
Read more
Scientists have engineered a bacterium whose genetic material includes an added pair of DNA 'letters', or bases, not found in nature. The cells of this unique bacterium can replicate the unnatural DNA bases more or less normally, for as long as the molecular building blocks are supplied.
May 7th, 2014
Read more
 Researchers at The University of Akron are again spinning inspiration from spider silk - this time to create more efficient and stronger commercial and biomedical adhesives that could, for example, potentially attach tendons to bones or bind fractures.
Researchers at The University of Akron are again spinning inspiration from spider silk - this time to create more efficient and stronger commercial and biomedical adhesives that could, for example, potentially attach tendons to bones or bind fractures.
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed






