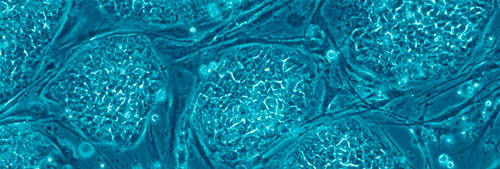
 Human stem cell research holds promise for combating some of the most recalcitrant of diseases and for regenerating damaged bodies. It is also an ethical, legal and political minefield.
Human stem cell research holds promise for combating some of the most recalcitrant of diseases and for regenerating damaged bodies. It is also an ethical, legal and political minefield.
Oct 28th, 2014
Read more
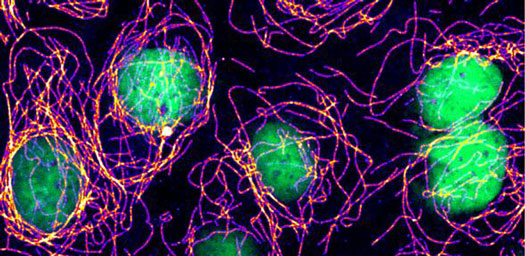 A new study at the University of Cambridge has allowed researchers to peer into unexplored regions of the genome and understand for the first time the role played by more than 250 genes key to cell growth and development.
A new study at the University of Cambridge has allowed researchers to peer into unexplored regions of the genome and understand for the first time the role played by more than 250 genes key to cell growth and development.
Oct 27th, 2014
Read more
A living cell, from one point of view, is a sort of sprawling protein factory that can churn out thousands of different proteins to order. Researchers are building on the basic idea of creating 'artificial cells' that might, in the future, enable us to control the production of proteins or other complex biological processes.
Oct 27th, 2014
Read more
A self-driven reaction can assemble phospholipid membranes like those that enclose cells.
Oct 27th, 2014
Read more
Two new studies shed light on how cells sense and respond to chemical trails.
Oct 27th, 2014
Read more
The scaffolds have desirable mechanical and biological properties at the same time, and due to the existence of the bladder tissue at tiny scale instead of cell, they do not require cell extraction or culture.
Oct 27th, 2014
Read more
Researchers report that they have made a breakthrough in understanding how a powerful antibiotic agent is made in nature. Their discovery solves a decades-old mystery, and opens up new avenues of research into thousands of similar molecules, many of which are likely to be medically useful.
Oct 26th, 2014
Read more
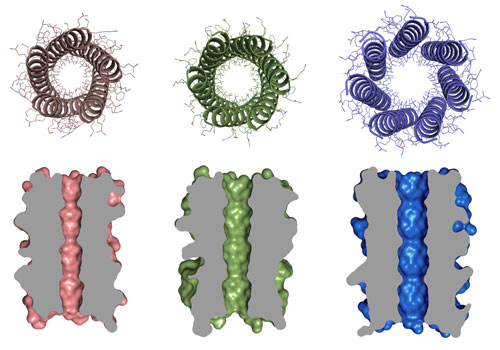 The scientists have made proteins with central cavities, or channels, running through them. The team believes that these will be useful in designing new protein functions, such as catalysts for breaking down fats, or molecules that span cell membranes to allow new communications between cells.
The scientists have made proteins with central cavities, or channels, running through them. The team believes that these will be useful in designing new protein functions, such as catalysts for breaking down fats, or molecules that span cell membranes to allow new communications between cells.
Oct 24th, 2014
Read more
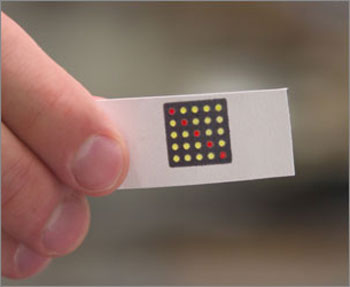 By combining efforts and innovations, Wyss Institute scientists develop synthetic gene controls for programmable diagnostics and biosensors, delivered out of the lab on pocket-sized slips of paper.
By combining efforts and innovations, Wyss Institute scientists develop synthetic gene controls for programmable diagnostics and biosensors, delivered out of the lab on pocket-sized slips of paper.
Oct 23rd, 2014
Read more
Researchers developed several new components for biological circuits. These components are key building blocks for constructing precisely functioning and programmable bio-computers.
Oct 23rd, 2014
Read more
New grants for five research projects awarded by the Bertarelli Program in Translational Neuroscience and Neuroengineering.
Oct 23rd, 2014
Read more
 An invasive seaweed clogging up British coasts could be a blessing in disguise. Scientists have won a cash award to turn it into valuable compounds which can lead to new, life-saving drugs.
An invasive seaweed clogging up British coasts could be a blessing in disguise. Scientists have won a cash award to turn it into valuable compounds which can lead to new, life-saving drugs.
Oct 22nd, 2014
Read more
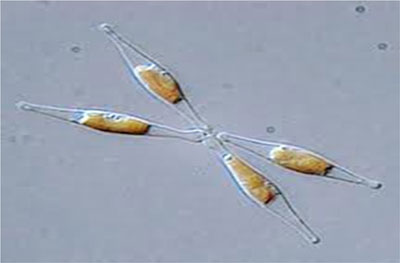 Researchers have discovered that blue and red light sensing photoreceptors control the carbon flow in diatoms.
Researchers have discovered that blue and red light sensing photoreceptors control the carbon flow in diatoms.
Oct 20th, 2014
Read more
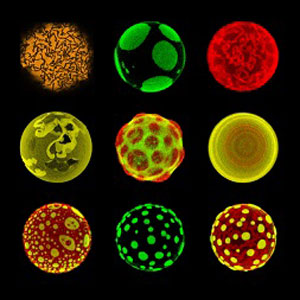 How did life originate? And can scientists create life? These questions not only occupy the minds of scientists interested in the origin of life, but also researchers working with technology of the future. If we can create artificial living systems, we may not only understand the origin of life - we can also revolutionize the future of technology.
How did life originate? And can scientists create life? These questions not only occupy the minds of scientists interested in the origin of life, but also researchers working with technology of the future. If we can create artificial living systems, we may not only understand the origin of life - we can also revolutionize the future of technology.
Oct 20th, 2014
Read more
Scientists hope a major breakthrough could lead to more effective methods for detoxifying dangerous pollutants like PCBs and dioxins. The result is a culmination of 15 years of research and has been published in Nature. It details how certain organisms manage to lower the toxicity of pollutants.
Oct 19th, 2014
Read more
 Organisms require flexible genomes in order to adapt to changes in the environment. Scientists have studied genomes of entire populations. They want to know why individuals differ from each other and how these differences are encoded in the DNA. In two review papers they discuss why DNA sequencing of entire groups can be an efficient and cost-effective way to answer these questions.
Organisms require flexible genomes in order to adapt to changes in the environment. Scientists have studied genomes of entire populations. They want to know why individuals differ from each other and how these differences are encoded in the DNA. In two review papers they discuss why DNA sequencing of entire groups can be an efficient and cost-effective way to answer these questions.
Oct 17th, 2014
Read more
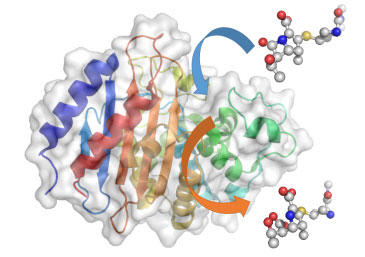 Scientists have used computer simulations to show how bacteria are able to destroy antibiotics - a breakthrough which will help develop drugs which can effectively tackle infections in the future.
Scientists have used computer simulations to show how bacteria are able to destroy antibiotics - a breakthrough which will help develop drugs which can effectively tackle infections in the future.
Oct 17th, 2014
Read more
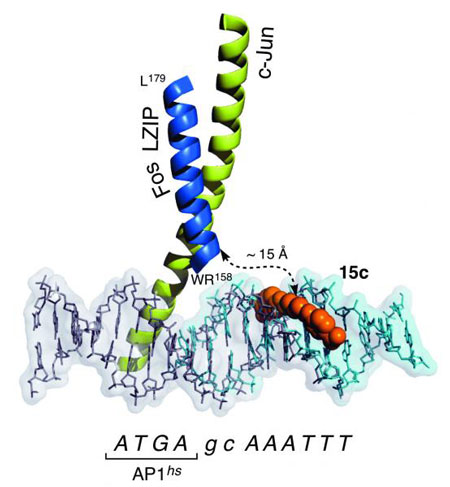 Researchers have introduced a new approach for achieving a highly selective, recognition of designed nine DNA base pairs. The strategy involves the nickel-promoted assembly of a peptide derived from a transcription factor, and a small molecule equipped with a metal-binding unit that acts as heterodimerizing staple.
Researchers have introduced a new approach for achieving a highly selective, recognition of designed nine DNA base pairs. The strategy involves the nickel-promoted assembly of a peptide derived from a transcription factor, and a small molecule equipped with a metal-binding unit that acts as heterodimerizing staple.
Oct 16th, 2014
Read more
 Human stem cell research holds promise for combating some of the most recalcitrant of diseases and for regenerating damaged bodies. It is also an ethical, legal and political minefield.
Human stem cell research holds promise for combating some of the most recalcitrant of diseases and for regenerating damaged bodies. It is also an ethical, legal and political minefield.
 Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed
Subscribe to our Biotechnology News feed







